91 Copyright © Acronis, Inc., 2000-2009
• access all Windows Restore Points on the recovered disk,
• access VSS snapshots via Windows Vista's "Previous Versions" feature on the recovered
disk,
• keep licensing and other information for installed appliacations as some programs may
use NT disk signature for licensing and other purposes,
• keep the existing scheduled task without the need to re-create or edit it, as all
scheduled tasks of the program use the NT disk signature for disk identification.
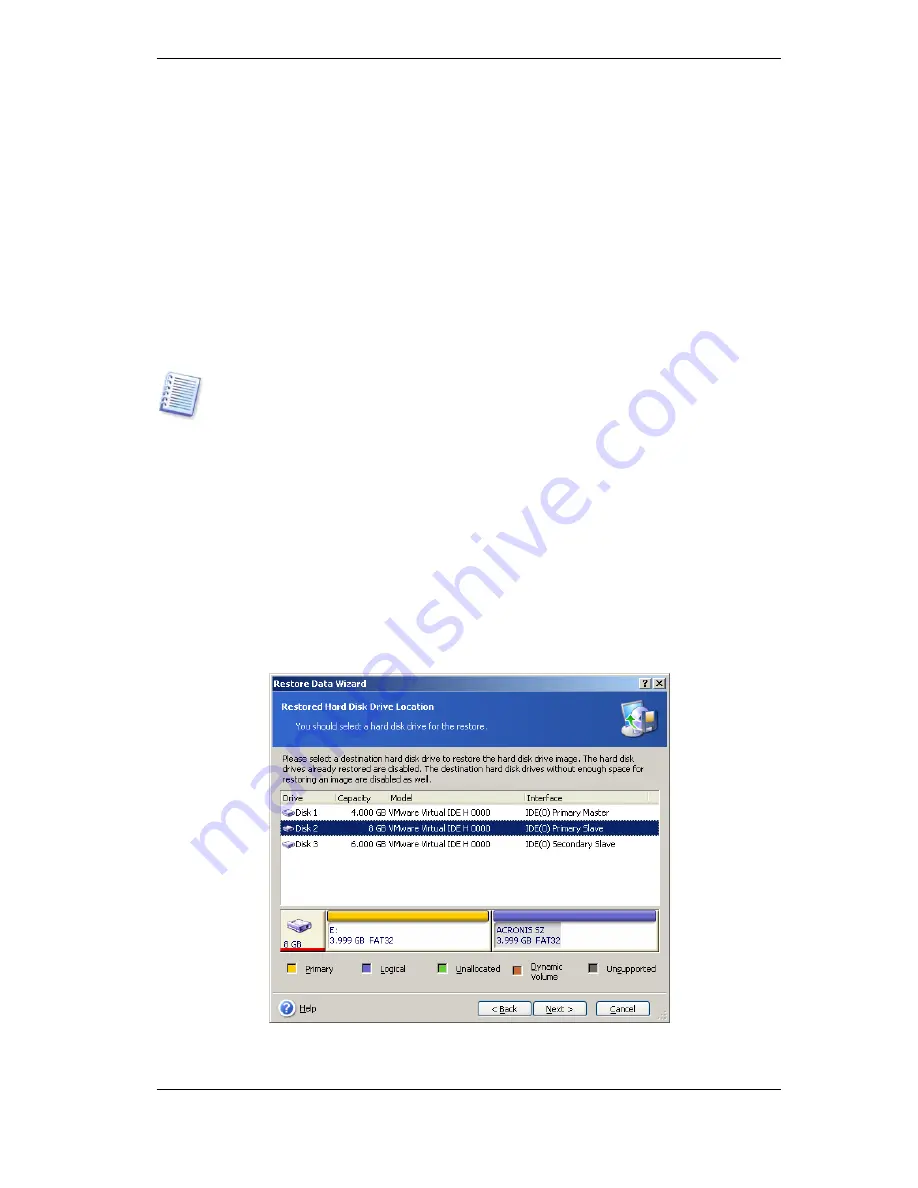
7.3.6 Selecting a target disk/partition
1. Select a target disk or partition where you want to deploy the selected image. You can
restore data to its initial location, to another disk/partition or to an unallocated space. The
target partition should be at least the same size as the uncompressed image data.
All the data stored on the target partition will be replaced by the image data, so be
careful and watch for non-backed-up data that you might need.
When restoring a Windows system disk and select a target disk, the program compares
critical for the system start devices, found in the image registry and the target computer
registry.
If the chipset, motherboard or mass storage device are different, there is a risk that the
system will not be able to boot. Then you will be prompted whether you want to buy
Acronis Universal Restore
. To find out more about this option, see
3.7 Acronis
Universal Restore
. To buy the option, follow the link.
If you already have Acronis Universal Restore, the prompt will not come up and you will
have an option to enable Acronis Universal Restore later in the Restore Data Wizard.
2. When restoring an entire disk, the program will analyze the target disk structure to see
if the disk is free.
















































