SERIES PMC230 PCI MEZZANINE CARD 16-BIT HIGH-DENSITY ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE
___________________________________________________________________________________________
- 7 -
32-bit access is not used by the PMC230. A 32-bit read will return
logic “0” for the most significant word.
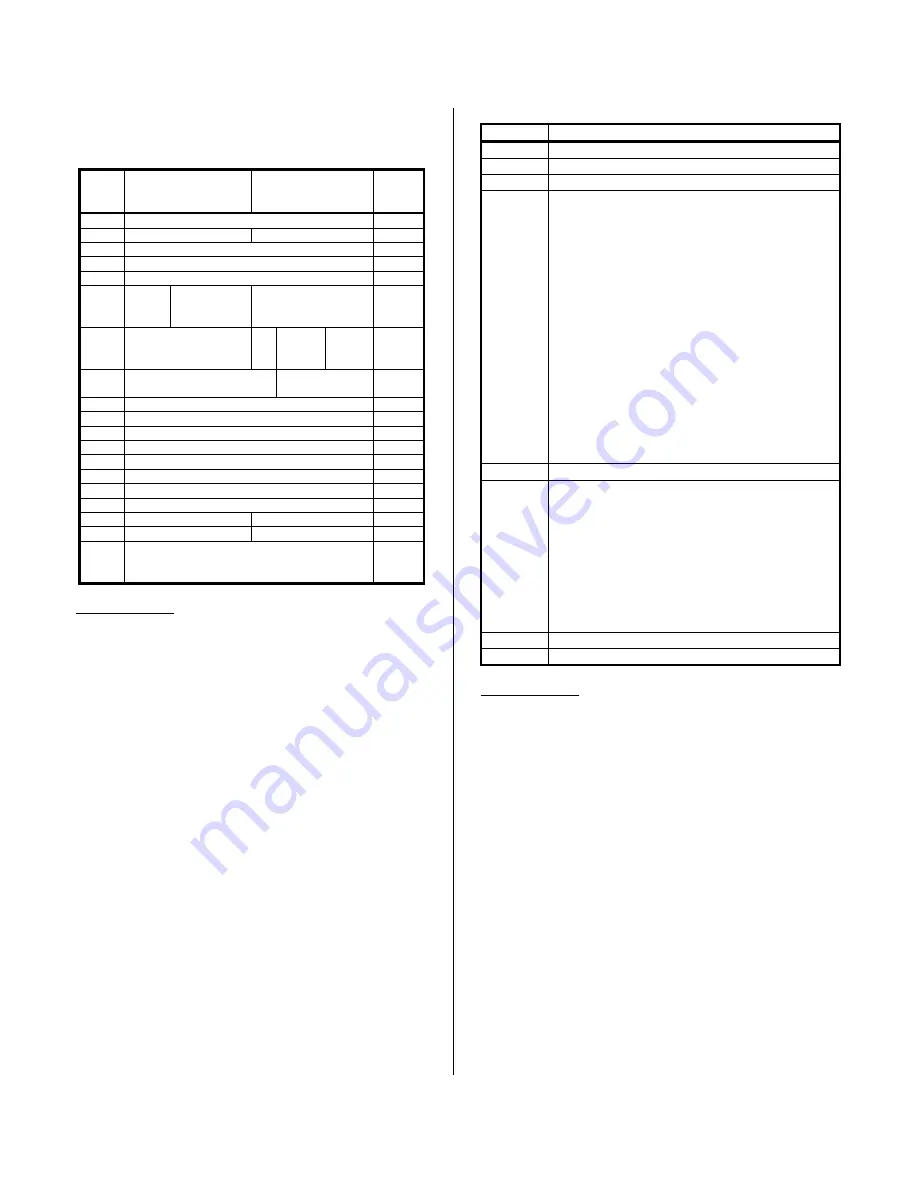
Table 3.2: PMC230 Memory Map
Hex
Base
Adr+
MSB
D15 D08
LSB
D07 D00
Hex
Base
Adr+
201
Control Register
200
205
Not Used
1
Not
Used
1
204
209
Not Used
1
208
20D
Not Used
1
20C
211
Not Used
1
210
215
Rd
Wr~
Calibration
Coefficient
Address
Calibration
Coefficient Write
Data
214
219
Calibration
Coefficient Read
Data
Wr
Busy
Rd
Comp
218
21D
Not Used
Bits15 to Bit 01
Start Convert
Bit-0
21C
221
DAC Channel 0
220
225
DAC Channel 1
224
229
DAC Channel 2
228
22D
DAC Channel 3
22C
231
DAC Channel 4
230
235
DAC Channel 5
234
239
DAC Channel 6
238
23D
DAC Channel 7
23C
241
Not Used
1
Not
Used
1
240
245
Reserved
2
Not
Used
1
244
249
↓
2FD
NOT USED
1
248
↓
2FC
Notes (Table 3.2):
1.
The PMC will respond to addresses that are "Not Used".
2.
This byte is reserved for use at the factory to enable writing of
the calibration coefficients.
3.
All writes are 8 clock cycles (except when a previous write is in
progress. In this case the write cycle will disconnect with
retry).
4.
All initial reads will disconnect without data and a retry will be
issued.
This memory map reflects byte accesses using the “Little
Endian” byte ordering format. Little Endian uses even-byte
addresses to store the low-order byte. The Intel x86 family of
microprocessors uses “Little Endian” byte ordering. Big Endian is
the convention used in the Motorola 68000 microprocessor family
and is the VMEbus convention. In Big Endian, the lower-order byte
is stored at odd-byte addresses.
Control Register, (Read/Write) - (Base + 200H)
This read/write register is used to: control the external trigger,
select one of the digital-to-analog conversion modes, and issue a
software reset.
The function of each of the control register bits are described in
Table 3.3. This register can be read or written with either 8-bit or
16-bit data transfers. A power-up or system reset sets all control
register bits to 0.
Table 3.3: Control Register
BIT FUNCTION
2,1,0 Not
Used
1
3 Not
Used
1
4 Not
Used
1
6, 5
External Trigger Control
00 = External Trigger Input:
External and Software triggers are all
enabled
01 = External Trigger Input:
External triggers are only enabled.
Software triggers are disabled.
10 = External Trigger Output:
Software triggers are output on the External
trigger pin of the field I/O connector. It is
possible to synchronize the conversion of multiple
PMC230 modules. A single master PMC230 must
be selected to output the external trigger signal (bit 6
and 5 set to “10”) while all other modules are selected
to input the external trigger signal (bit 6 and 5 set to
“01”). The external trigger signals (pin 49 of the field
I/O connector) of all modules to be synchronized
must be wired together.
7 Not
Used
1
10, 9, 8
DAC Conversion Mode
000 = Disabled
001 = Single Conversion from DAC registers
010 = Not Defined
011 = Not Defined
100 = Not Defined
101 = Not Defined
110, 111 = Not Defined
All modes require either the software start convert or
an external trigger to initiate DAC conversions.
11 to 14
Not Used
2
15
Perform Software Reset when Set
2
Notes (Table 3.3):
1. All bits labeled “Not Used” will return the last value written on a
read access.
2. Bits 11 to 15 will return random values when read.
Calibration Coefficient Access Register (Write, 215H)
This register configures access to the calibration coefficient
memory. Calibration data is provided so that software can adjust
and improve the accuracy of the analog output voltage over the
uncalibrated state. Each channel’s unique offset and gain
calibration coefficients are stored in this memory. These coefficients
can be retrieved using this register.
The Calibration Coefficient Access Register is a write-only
register and is used to configure and initiate a read cycle to the
calibration coefficient memory. Setting bit-15 of this register high, to
a “1’’, initiates a read cycle.
The address of the calibration coefficient to be read must be
specified on bits 14 to 8 of Calibration Coefficient Access register.
The address location of each of the gain and offset coefficients is
given in table 3.4.
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com








































