BusWorks
Model 903MB/902MB/901MB Network I/O Module User’s Manual Digital I/O
___________________________________________________________________________________________
- 18 -
Testing Your Configuration
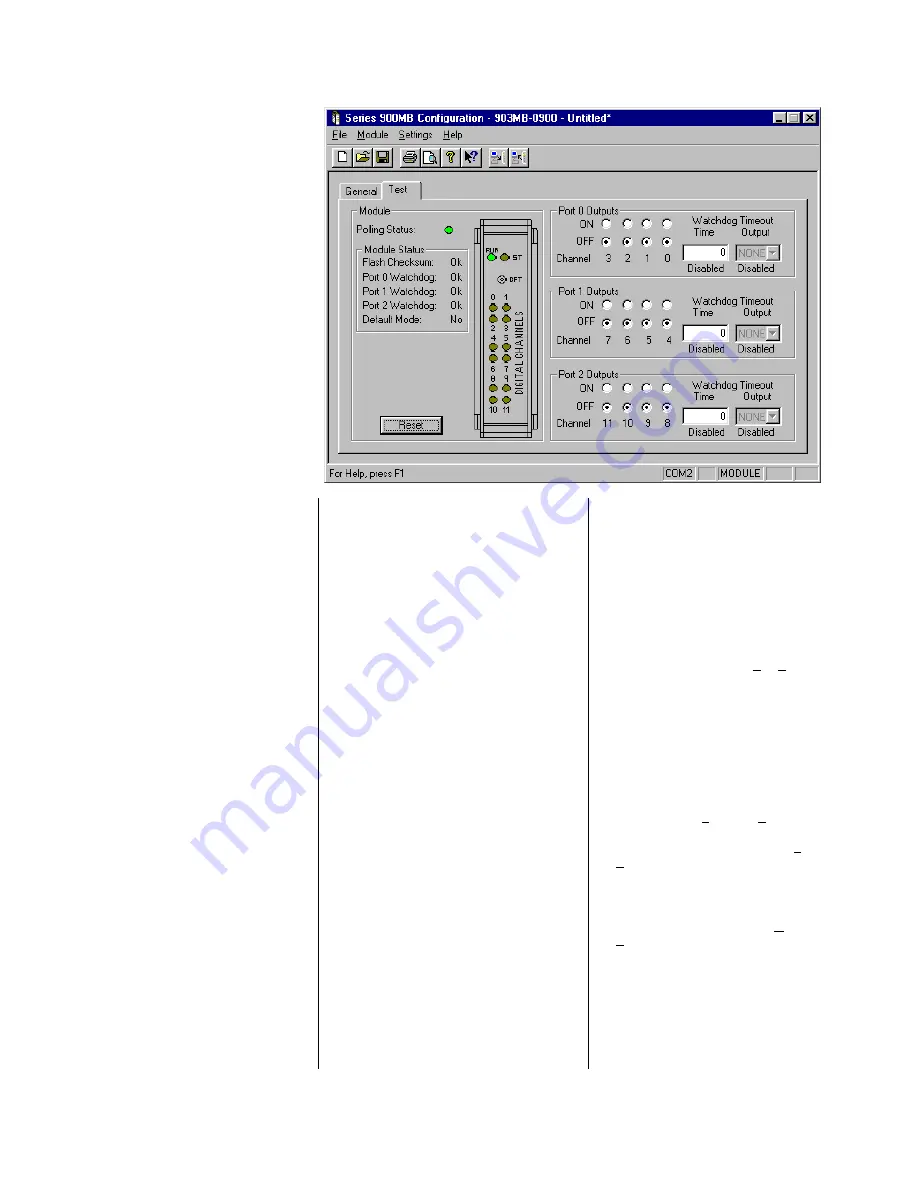
The “Test” portion of this program
allows you to monitor polling, module
status flags, reset the module, control
output states, and monitor input states.
This page is also used to configure the
port watchdog time and the timeout
reset states for the port.
Port I/O Watchdog Timer
The right half of this screen allows you
to configure the Port I/O Watchdog
Timer. A watchdog timeout is triggered
if no channel read or write occurs for
one or more port channels, within the
timeout period specified. A timeout is
cleared and the timer reinitiated when a
port channel read or write occurs. Note
that clearing a timeout does not return
the outputs to their pre-timeout state.
They will retain their current state until
otherwise written.
Use the port 0, 1, & 2
“Timeout
Output”
scroll bar to select the timeout
binary pattern to program the port
outputs to following a timeout. A pattern
of four bits is selected via this scroll bar
and represents the ON (1) and OFF (0)
states the port output channels are to
be sent to following a watchdog timeout.
The lsb corresponds to the lowest
numbered port channel. Select “None”
if you want the port outputs to remain in
their current states upon timeout.
Use the port 0, 1, & 2
“Watchdog
Time”
field to specify a watchdog
timeout period up to 65534 seconds
(18.2 hours). A value of 0 or 65535 will
disable the port watchdog function and
“Disabled” will be indicated below the
Watchdog Time field.
Note that when this screen is selected,
the module channels are continuously
polled. Thus, you are not likely to ever
encounter a watchdog timeout with this
screen displayed.
Testing Your Operation
This screen also allows you to monitor
polling, module status flags, reset the
module, control output states, and
monitor input states.
For each I/O channel, the current true
input state is reflected via the simulated
LED’s of the module graphics. These
LED’s match the LED’s on the front of
the module.
For 903MB models, input buffers are
connected in tandem with open-drain
outputs for convenient loopback
monitoring of the output state. The
source leads of each port output
channel are tied in common to the port
return lead (RTN). The drain leads are
pulled up to the port excitation terminal
via resistor SIP’s installed in sockets at
each port. An external excitation supply
must be connected between the port
EXC and RTN terminals. Turning an
output ON connects the I/O lead to
return via the output mosfet. The inputs
are active-low, as the outputs are open-
drain, low-side switches. The 901MB &
902MB are the same as the 903MB, but
the 901MB has outputs removed and
the 902MB has inputs removed.
The output state of each port output
channel is set via the “ON” or “OFF”
bullet (902MB & 903MB units only).
Simply click ON or OFF as desired to
turn the corresponding output ON or
OFF. The output state corresponds to
the gate signal of the output channel’s
mosfet and may not reflect the actual
state of the mosfet’s source lead if the
drain is left open or floating. The actual
output state of the 906MB is obtained
via the simulated module LED’s, as the
input buffer is tied directly to the drain of
the output mosfet which connects to the
output terminal. Thus, for 903B models,
the input state reflects the actual state
of the open-drain output for the tandem
I/O channel via closed-loop feedback.
However, on 902MB models, input
circuitry is removed and the input state
is assumed equivalent to the output
state as it reflects the gate signal of the
corresponding output mosfet. Thus, the
902MB LED’s are driven via the gate
signal and not the actual output signal.
Print Your Configuration
If you wish to document your transmitter
configuration, then select
File-Print
to
get a two page printout of all of your
selected configuration parameters.
Saving Your Configuration
Note that the currently loaded
configuration file name is indicated at
the top of the screen to the right of the
model number.
You may select
File-Save As
to save
your configuration file to disk and give it
a new file name. Otherwise, use File-
Save to save the current file without
renaming it.
In the event that you lose a
configuration file, you can always
upload it from the module via Module-
Upload Configuration.
Note that the configuration process will
vary slightly for other model types.
Now wasn’t that easy! That’s all there is
to using the Configuration software to
configure your module. The module is
now ready for installation in the field.

























