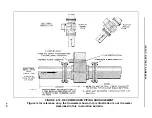
The conductivity of the process liquid (in microsiemens/cm) may be determined from the electrode ac
resistance measurement (in megohms) by substitution of values in the following equation.
σ
=
1
(R
ac
- 0.072) x Electrode Diameter, in cm
where,
0.072 is the electrode barrier resistance in megohms; i.e., 36 k
Ω
x 2/10
6
and,
typical electrode diameter is 0.77 cm
For example, assuming the measured ac electrode resistance (full pipe) is 192,000 ohms and
electrode diameter is 0.76 cm, then
σ
=
1 = 10.82
µ
S/cm
(0.192 - 0.072) x 0.77
This is above the threshold for specified measurement accuracy for the particular liquid, meter size
and signal converter combination. Liquid conductivities at the operating temperature may also be
determined from standard references for many pure liquids. Factory Field Engineers are equipped to
determine the conductivities of special liquids at the user’s site.
Electrode diameters vary with meter size and type of liner, the values given in Table 4-1 are typical
electrode diameters.
TABLE 4-1. ELECTRODE DIAMETERS
Meter Size
inches (mm)
Electrode Diameters
TEFLON Lined Meter
Neo/Poly Lined Meter
1 - 1
1
⁄
2
(25-40)
.770 cm (.303 inch)
------------
2 - 4 (50-100)
.820 cm (.323 inch)
.635 cm (.250 inch)
6 - 12 (150-300)
1.200 cm (.472 inch)
.635 cm (.250 inch)
10DS3111E INSTRUCTION MANUAL
4-4