ZXR10 8900E series Core Switch Product Description
36
© 2013ZTE CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
and speed are greatly improved with the development of network technology, the data
needs transmission is increasing as fast as network development. At the same time,
some new applications emerged in recent years (such as multimedia and multicast) not
only add to network traffic but also change the traffic on the Internet. They need
brand-new service requirements. Without service quality guarantee, bandwidth
reservation, and restricted network delay, the network cannot support the applications
sensitive to indexes of bandwidth, delay, jitter and packet loss ratio such as VoIP, video
conference, Providing capability to support QoS is a feasible measure to solve the
problem. QoS aims to provide different service quality for various applications with
different needs such as providing private bandwidth, reduce packet loss ratio, reduce
packet transport delay and jitter.
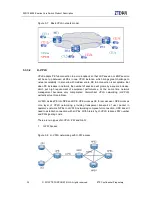
QoS works to effectively provide users with E2E service quality control or guarantee.
QoS enables network unit (such as program, host or network equipment) can guarantee
its service flow and service requirements are satisfied at a certain level. QoS can control
various network applications and satisfy multiple network application requirements. For
example:
To control the resource: to restrict bandwidth used by FTP on backbone network, or to
offer higher priority to database access.
Cuttable services: subscribers of ISP (Internet Service Provider) can transport voice,
video or other realtime services. QoS can make ISP distinguish these different packets
and provide different services.
Co-existence of multiple needs: be able to provide bandwidth and low delay guarantee
for time-sensitive multimedia services. Other services in operation will not influence these
time-sensitive services.
QoS doesn’t create bandwidth. It only manages bandwidth based on program needs and
network situation. QoS has a series performance indexes including the following:
Service availability: the reliability of the connection between subscribers and Internet
service.
Transmission delay: time interval of data packets transmitting and receiving between two
reference points.
Variable delay: also called jitter, is the time difference between data packets in a group of
data flow transmitted on one route.
Throughput: rate of data packets transmitted in the network, which can be represented in
average rate or peak rate.
Packet loss ratio: the highest ratio of data packet loss in network. Data packet loss is
usually caused by network congestion.
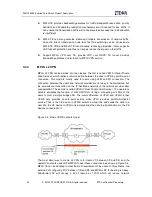
ZXR10 8900E series provides the following functions to realize the above objectives:
Содержание ZXR10 8900E series
Страница 1: ...Operator Logo ZXR10 8900E series Core Switch Product Description ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 10: ......