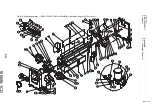
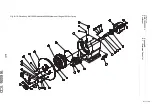
C-3
166006-1CD
166006-1CD
Appendix C
C
RM2-755/1255SL
Positioner
C
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Computer Aided Design (CAD). Computer graphic applications designed
to allow engineering of objects (or parts), which are to be manufactured. A
computer is used as a tool to design schematics and produce blueprints,
which enable the accurate production of the object. The CAD system
enables the three dimensional drawings of basic figures, exact sizing and
placement of components, making lines of specified length, width, or
angle, as well as satisfying varying geometric shapes. This system also
allows the designer to test a simulated part under different stresses, loads,
etc.
Cartesian Coordinates
Cartesian Coordinates is a type of coordinate system that specifies the
location of a point in two dimensional space by a pair of numerical
numbers, which further specify the distance to fixed axes that are
perpendicular to each other. In simple terms, an XY graph represents a
two dimensional Cartesian Coordinate System. When a point is specified
in a three dimensional space (XYZ graph), it constitutes a three
dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. A robot’s TCP position is
specified in a Cartesian Coordinate.
Cartesian Manipulator
A Cartesian Manipulator is a Manipulator arm with prismatic joints, which
allows movement along one or more of the three- axes in the X, Y, Z
coordinate system.
Cartesian Topology
A topology, which uses prismatic joints throughout, normally arranged to
be perpendicular to each other.
Cartesian-coordinate Robot
A Cartesian-coordinate Robot is a robot whose Manipulator-arm degrees
of freedom are defined by Cartesian Coordinates. This describes motions
that are east-west, north-south and up-down, as well as rotary motions to
change orientation.
Category 3 (Cat3)
Category 3 (Cat 3) means that the safety related parts of the control
system will be designed so that:
• Single faults will not prevent the safety function from working
correctly.
• Single faults will be detected at or before the next demand of the
safety function.
• When a single fault does occur, a safe state shall be maintained until
the detected fault is corrected.
• All reasonably foreseeable faults are detected.
Caution
Indicates a hazardous situation, which if not avoided, could result in minor
or moderate injury. It may also be used without the safety alert symbol as
an alternative to “NOTICE”.
120 of 145