SonTek, a Xylem brand
RiverSurveyor S5/M9 System Manual (February 2013)
57
Screening Distance –
This is the distance below the face of the ADP that you want to start col-
lecting data. In essence, this setting allows you to program the ADP to start collecting data be-
low a certain point. This is primarily used for over-the-boat applications where the screening
distance can be set to avoid flow disturbance from the wake of the boat.
7.6.3.
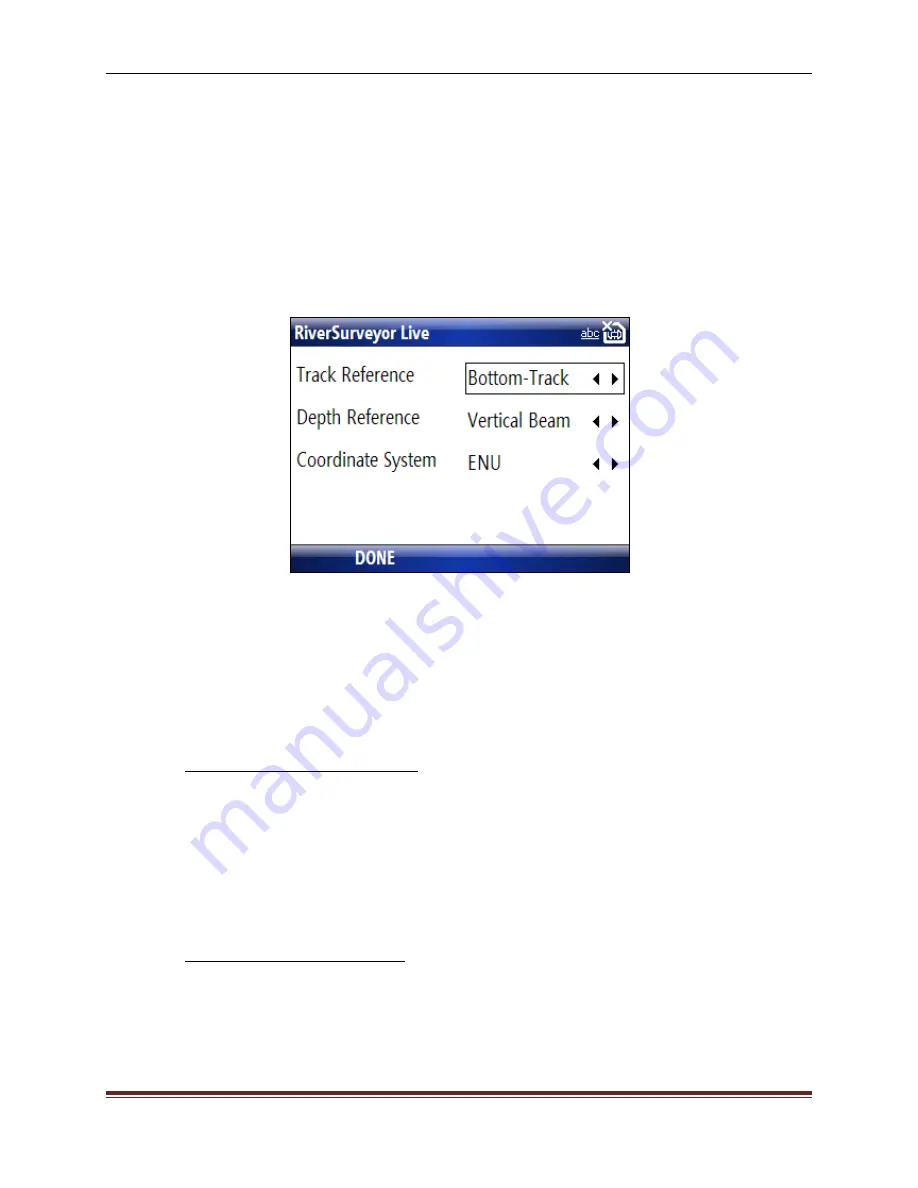
Track and Depth Reference (3)
The Track and Depth Reference menu (Figure 63) displays options for the track reference,
depth reference, and coordinate system. Use the up/down keys to move between fields. To
change an option in a field use the left/right keys. When finished, select
DONE
(at the bottom)
to
update the settings and return to the Main Menu.
Figure 63. Track and Depth Reference Menu
Track Reference
– The ADP measures a water velocity using the Doppler shift principle, using
multiple acoustic pulses transmitted and received throughout the water column. When the ADP
is in motion, the water velocity actually measured by the ADP is a combination of boat velocity
and water velocity. In order to determine true water velocity, the boat speed must be known
and then subtracted from the actual water velocity measurement. The RiverSurveyor “moving
boat” discharge application uses three methods (references) to determine boat velocity.
1.
Bottom-Track reference velocity: The ADP itself is capable of determining boat
speed using a technique called “ ”. In this case, bottom-track velocity is calculated
using the Doppler shift received from multiple acoustic pulses (transmitted from the
ADP) that have reflected off of the riverbed. If the riverbed is stationary (i.e. non-
moving bottom), then the Doppler shift velocity will consist entirely of boat speed ve-
locity which is acceptable for discharge calculations. If the riverbed is in motion the
Doppler-shift-based velocity will consist of both boat speed and riverbed speed which
will bias discharge calculations. In this case, the following two references would be
preferred to determine boat velocity.
2.
GGA GPS-referenced velocity: GPGGA (GGA) refers to a specific NMEA-0183 pro-
tocol for outputting GPS position data. In this case, the GGA “string” contains actual
position (latitude/longitude) information along with several other GPS quality parame-
ters. Boat velocity is calculated by measuring the distance between two successive
GGA positions divided by the travel time between those two positions. Differential
corrections are required for the GGA data to reduce the amount of position error as-
Содержание SonTek River Surveyor M9
Страница 10: ......
Страница 118: ......
Страница 150: ...SonTek a Xylem brand 140 RiverSurveyor S5 M9 System Manual February 2013 Figure 126 Island Edge...
















































