48
Chapter 11
Customize Your Network Settings
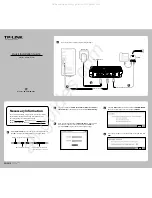
Destination IP:
The destination IP address that you want to assign to a static route. This IP address
cannot be on the same subnet with the WAN IP or LAN IP of the router. In the example, the IP
address of the company network is the destination IP address, so here enters 172.30.30.1.
Subnet Mask:
Determines the destination network with the destination IP address. If the destination
is a single IP address, enter 255.255.255.255; otherwise, enter the subnet mask of the corresponding
network IP. In the example, the destination network is a single IP, so here enters 255.255.255.255.
Gateway:
The IP address of the gateway device to which the data packets will be sent. This IP address
must be on the same subnet with the router’s IP which sends out the data. In the example, the
data packets will be sent to the LAN port of Router 2 and then to the Server, so the default gateway
should be 192.168.0.2.
Interface:
Determined by the port (WAN/LAN) that sends out the data packets. In the example, the
data is sent to the gateway through the LAN port, so LAN should be selected.
Status:
Determines the status of the entry. In the example, Enabled should be selected.
6. Click
OK
to save the settings.
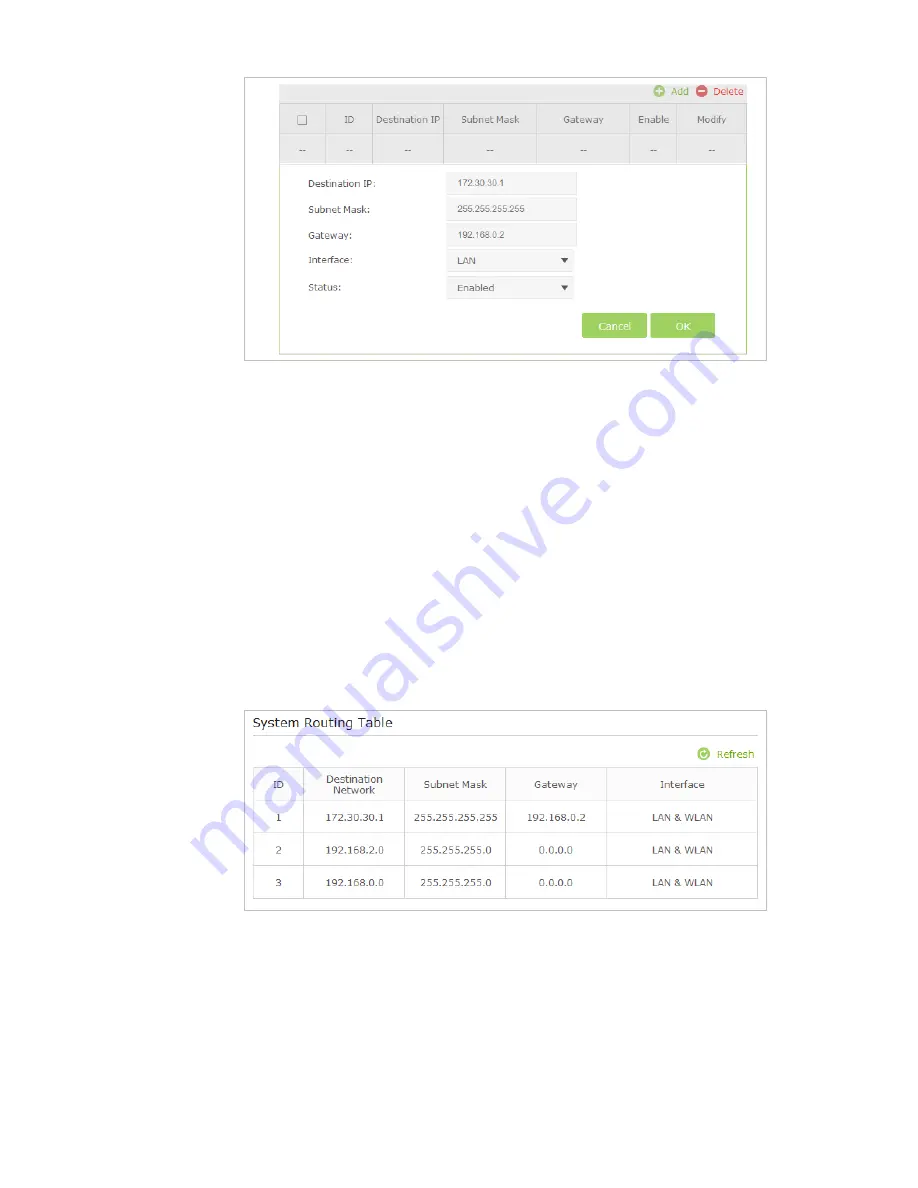
7. Check the
System Routing Table
below. If you can find the entry you set, the static routing is set
successfully.
Open a web browser on your PC. Enter the company server’s IP address to visit the company network.
11. 6. Specify Wireless Settings
The router’s wireless network names (SSIDs) and passwords, and security options are preset in the factory. The preset SSIDs
and passwords can be found on the product label. You can customize the wireless settings according to your needs.
1. Visit
http://tplinkwifi.net
, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
Done!