Maintenance— Type 1L20
the studs. If not, they can be pulled out separately. An
alternative method of removing the terminal strip is to use
diagonal cutters to cut o ff the sides o f the studs. The ceramic
strip is removed and the studs pulled from the chassis with
a pair o f pliers.
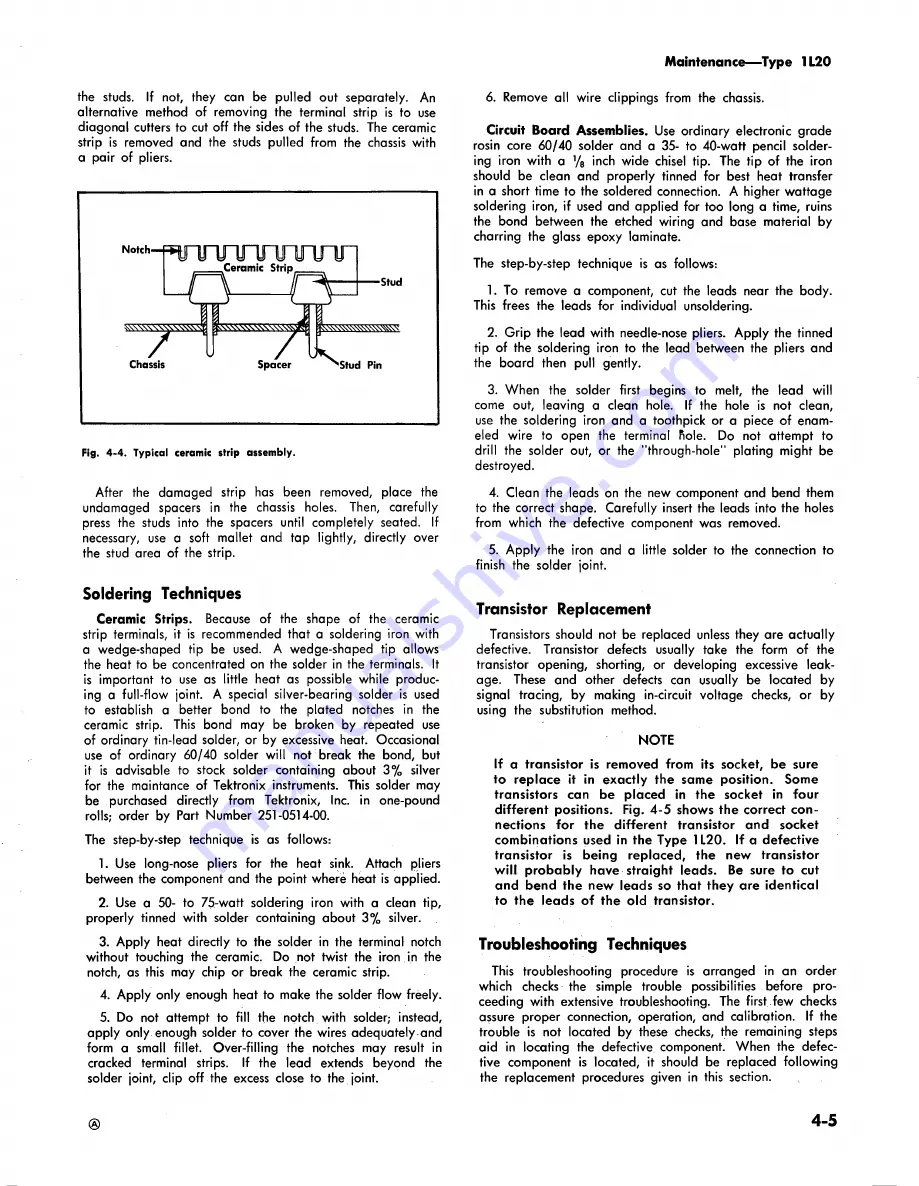
N°,'h- f s^nru~injH JTjij~Tr
Ceramic Strip
L-Q — Q = l
■Stud
y
Chassis
Spacer
Stud Pin
Fig. 4 -4 . Typical ceramic strip assembly.
After the damaged strip has been removed, place the
undamaged spacers in the chassis holes. Then, carefully
press the studs into the spacers until completely seated. If
necessary, use a soft mallet and tap lightly, directly over
the stud area of the strip.
6. Remove all wire clippings from the chassis.
Circuit Board Assemblies.
Use ordinary electronic grade
rosin core 60/40 solder and a 35- to 40-watt pencil solder
ing iron with a y8 inch wide chisel tip. The tip o f the iron
should be clean and properly tinned for best heat transfer
in a short time to the soldered connection. A higher wattage
soldering iron, if used and applied for too long a time, ruins
the bond between the etched wiring and base material by
charring the glass epoxy laminate.
The step-by-step technique is as follows:
1. To remove a component, cut the leads near the body.
This frees the leads for individual unsoldering.
2. G rip the lead with needle-nose pliers. A pply the tinned
tip of the soldering iron to the lead between the pliers and
the board then pull gently.
3. When the solder first begins to melt, the lead will
come out, leaving a clean hole. If the hole is not clean,
use the soldering iron and a toothpick or a piece o f enam
eled wire to open the terminal Role. Do not attempt to
drill the solder out, or the "through-hole" plating might be
destroyed.
4. Clean the leads on the new component and bend them
to the correct shape. Carefully insert the leads into the holes
from which the defective component was removed.
5. A pply the iron and a little solder to the connection to
finish the solder joint.
Soldering Techniques
Ceramic Strips. Because of the shape of the ceramic
strip terminals, it is recommended that a soldering iron with
a wedge-shaped tip be used. A wedge-shaped tip allows
the heat to be concentrated on the solder in the terminals. It
is important to use as little heat as possible while produc
ing a full-flow joint. A special silver-bearing solder is used
to establish a better bond to the plated notches in the
ceramic strip. This bond may be broken by repeated use
of ordinary tin-lead solder, or by excessive heat. Occasional
use of ordinary 60/40 solder w ill not break the bond, but
it is advisable to stock solder containing about 3% silver
for the maintance of Tektronix instruments. This solder may
be purchased directly from Tektronix, Inc. in one-pound
rolls; order by Part Number 251-0514-00.
The step-by-step technique is as follows:
1. Use long-nose pliers for the heat sink. Attach pliers
between the component and the point where heat is applied.
2. Use a 50- to 75-watt soldering iron with a clean tip,
properly tinned with solder containing about 3% silver.
3. Apply heat directly to the solder in the terminal notch
without touching the ceramic. Do not twist the iron in the
notch, as this may chip or break the ceramic strip.
4. Apply only enough heat to make the solder flow freely.
5. Do not attempt to fill the notch with solder; instead,
apply only enough solder to cover the wires adequately and
form a small fillet. O ver-filling the notches may result in
cracked terminal strips. If the lead extends beyond the
solder joint, clip o ff the excess close to the joint.
Transistor Replacement
Transistors should not be replaced unless they are actually
defective. Transistor defects usually take the form o f the
transistor opening, shorting, or developing excessive leak
age. These and other defects can usually be located by
signal tracing, by making in-circuit voltage checks, or by
using the substitution method.
NOTE
If a tra n sisto r is removed from its socket, be sure
to re p la ce it in e x a c tly the same po sitio n. Some
transistors can be placed in the socket in fo u r
d iffe re n t positions. Fig. 4 -5 shows the correct co n
nections fo r th e d iffe re n t transistor a nd socket
co m b in a tio n s used in the Type 1L20. If a d e fe ctive
tra n sisto r is being replaced, th e new tra n sisto r
w ill p ro b a b ly have s tra ig h t leads. Be sure to cut
and bend th e new leads so th a t th e y are id e n tic a l
to th e leads o f th e o ld transistor.
Troubleshooting Techniques
This troubleshooting procedure is arranged in an order
which checks the simple trouble possibilities before pro
ceeding with extensive troubleshooting. The first few checks
assure proper connection, operation, and calibration. If the
trouble is not located by these checks, the remaining steps
aid in locating the defective component. When the defec
tive component is located, it should be replaced follow ing
the replacement procedures given in this section.
4 -5
Содержание 1L20
Страница 4: ...Type 1L20 Fig 1 1 Type 1L20 Spectrum Analyzer...
Страница 16: ...NOTES...
Страница 18: ...Fig 3 1 Block Diagram of the Type 1L20 N Circuit Description Type 1L20...
Страница 32: ...Maintenance Type 1L20 4 10 Fig 4 6 Phase Lock and Recorder Detector Circuit Boards...
Страница 42: ...Calibration Type 1L20 4B 40 4D 4E 6 2 Fig 6 1 Recommended equipment for calibrating the Type 1L20...
Страница 43: ...Calibration Type 1L20 10 11 12 13 14 15 6 3 Fig 6 2 Recommended Calibration tools and equipment...
Страница 94: ......
Страница 97: ...N0I133S 3H ZHU i...
Страница 98: ...TYPE IL LO SPECTRUM ANALYZER A P H A S E LO C K U S C IR C U IT 2 PHASE LOCK CIRCUIT...
Страница 100: ...T 1 SW EEPER CIRCUITS...
Страница 102: ...N B IFA M PL 70 MHz OSC 6...
Страница 103: ...I o o z o o 5 1166 TYPE IL Z 0 IL 3 0 SPEC TR U M ANALYZER A VARIABLE RESOLUTION CIRCUITS T V A R IA B L E RESOL...
Страница 104: ...5 M H z AM PLIFIE R D E TECTO RS TYPE IL Z O IL 3 0 S P E C T R U M ANALYZER A OUTPUT AMPLIFIER OUTPUT AMPLIFIER...
Страница 105: ...TYPE 1L20 SPECTRUM ANALYZER...
Страница 106: ...FIG 2 REAR CHASSIS TYPE 1L20 SPECTRUM ANALYZER 1 F IG 2...
Страница 107: ...FIG 3 IF CHASSIS T i T L A TYPE 1L20 SPECTRUM ANALYZER F I G 3...
Страница 108: ...FIG 4 LOW PASS FILTER PHASE LOCK ASSEMBLY FIG 4...
Страница 110: ...OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES TYPE 1L20 SPECTRUM ANALYZER...
Страница 112: ...TYPE 1L20 TYPE 1L30 PARTS LIST CORRECTION CHANGE TO R823 30 0181 00 180 a 1W 10 Cl 366...