36
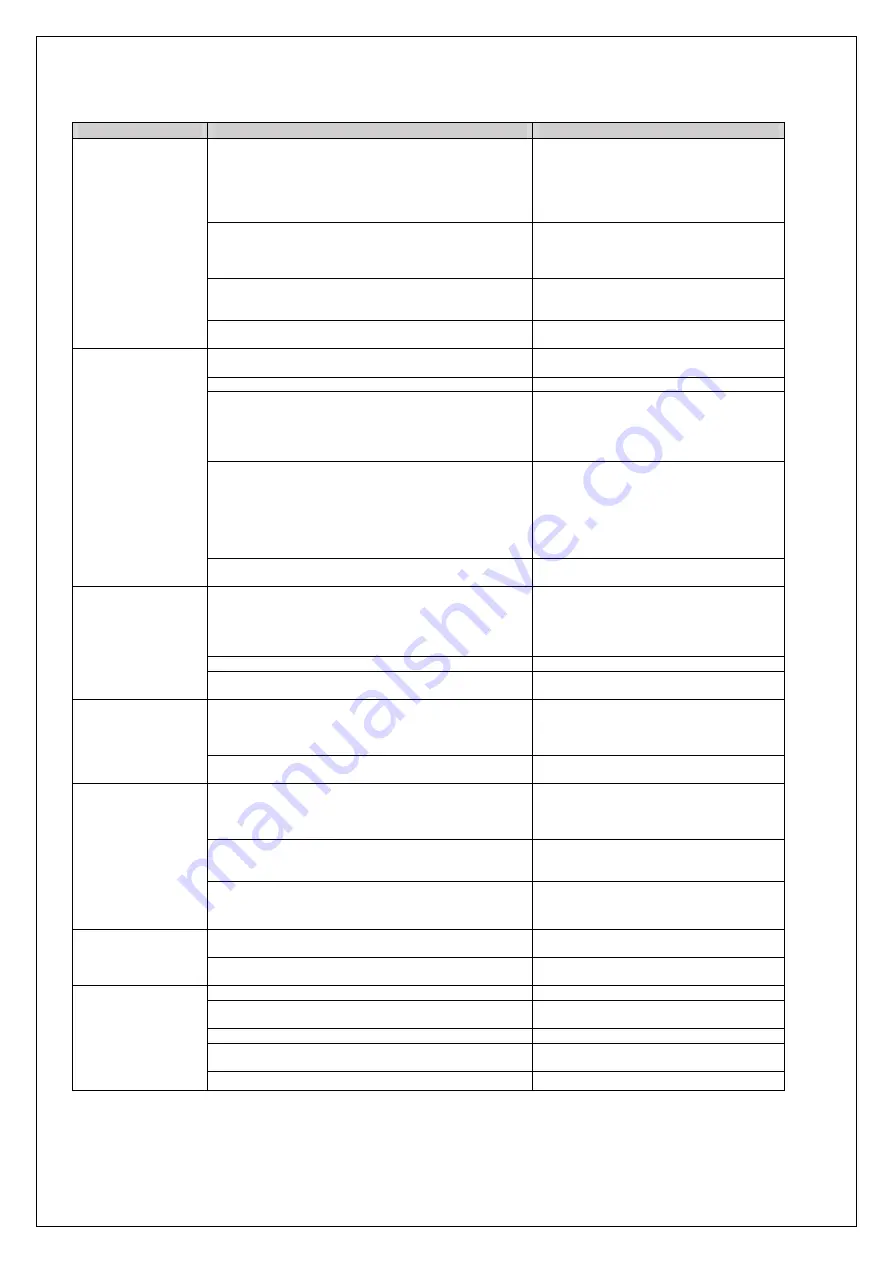
Table 3.2 Drive problems and corrective actions
Problem
Control Mode and Possible Cause
Corrective Action
Rollback at start
Insufficient torque when the brake is released.
• Increase the DC Injection Braking Current at
Start using parameter S1-02.
•Increase Torque Detection Gain (C4-01) in
steps of 0.2.
•Increase starting frequency (S1-00).
•Increase Voltage offset (E1-03) in steps of 5V.
DC Injection and brake timing are not optimized.
Set the time for DC Injection Braking at Start
(S1-04) as short as possible, and make sure that
brake releases completely before the motor starts
to turn.
Motor torque is not fully established when the brake is released.
Lengthen the Brake Release Delay Time (S1-06)
and the time for DC Injection Braking / Position
Lock at Start (S1-04).
Motor contactor closes too late.
Make sure that the contactors are closed before
the Up/Down command is issued.
Shock at start
Motor starts rotating when the brake is not completely released
or runs against the brake.
Increase the DC Injection Braking Time at Start
using parameter S1-04.
Acceleration rate is changing too quickly.
Increase C2-01.
Starting torque influences the calculated slip.
•Increase Slip Compensation Filter Time
Constant (S2-06).
•If the problem exists, increase the Slip
Compensation Delay Time (S2-05) in steps of
50ms.
Starting torque is too much.
•Increase Torque Detection Delay Time (C4-02)
in steps of 50ms.
• If the problem still exists, decrease Torque
Detection Gain (C4-01). Note that decreasing
C4-01 may result in motor stall and over-current
fault. In this case, increase acceleration time
(C1-01).
The starting speed is not optimized.
Change S1-00 in steps of 0.1, and see its
influence on shock.
Shock at stop
Brake is applied too early, causing the motor to run against the
brake.
•Increase the Delay Time to Close the Brake
(S1-07). If necessary, also increase the DC
Injection Braking Time at Stop S1-05.
•If the problem still exists, increase zero speed at
stop (S1-01).
Motor contactor is released before the brake is fully applied.
Check the motor contactor sequence. (S1-11)
DC injection is not powerful enough to stop the motor
efficiently.
Increase DC injection at stop (S1-03).
Jerk occurs due to
overshoot when the
motor reaches top
speed.
Too fast torque or slip compensation.
• Increase the Torque Compensation Delay Time
(C4-02).
• Increase the Slip Compensation Delay Time
(S2-06).
The acceleration rate changes too quickly when reaching the
selected speed.
Decrease the Jerk at the End of Acceleration.
Increase C2-02.
Motor stops shortly
(undershoot) when
the leveling speed is
reached.
Not enough torque at low speed.
If (E1-02=0), change it to 1 or 3.
If E2-02=1, Increase E1-03.
If E2-02=2/3, Increase (E1-10 to E1-13).
Alternatively, you may increase E1-03.
Too much slip compensation.
Adjust the motor data, especially motor rated
speed (S2-01) correctly.
The deceleration rate changes too quickly when reaching
leveling speed.
Decrease the Jerk at the End of Deceleration.
Increase C2-04.
Motor or machine
vibrates at high
speed or top speed.
Torque compensation responds too quickly.
Increase the Torque Compensation Delay Time
(C4-02).
Rated speed is not set correctly
Set the rated speed according to the motor
nameplate.
Motor or machine
vibrates in the low
or medium speed
range.
The output voltage is too high.
Set E2-02 to 2or 3 and decrease E1-10 to E1-13.
Torque compensation is responding too quickly.
Increase the Torque Compensation Delay Time
(C4-02).
The value for the motor slip is set incorrectly.
Check the Motor Slip value in parameter E2-02.
The slip fluctuation is high.
Increase the Slip Compensation Filter Time (S2-
06) in steps of 50ms.
Vibration occurs only in regenerative mode.
Increase C4-01.
Table 3.3 Drive problems and corrective actions (closed-loop)
Содержание L450S
Страница 1: ...User Manual L450U L450S...
Страница 5: ...7 Figure 2 2 b SBT L450S I O block diagram...







































