35
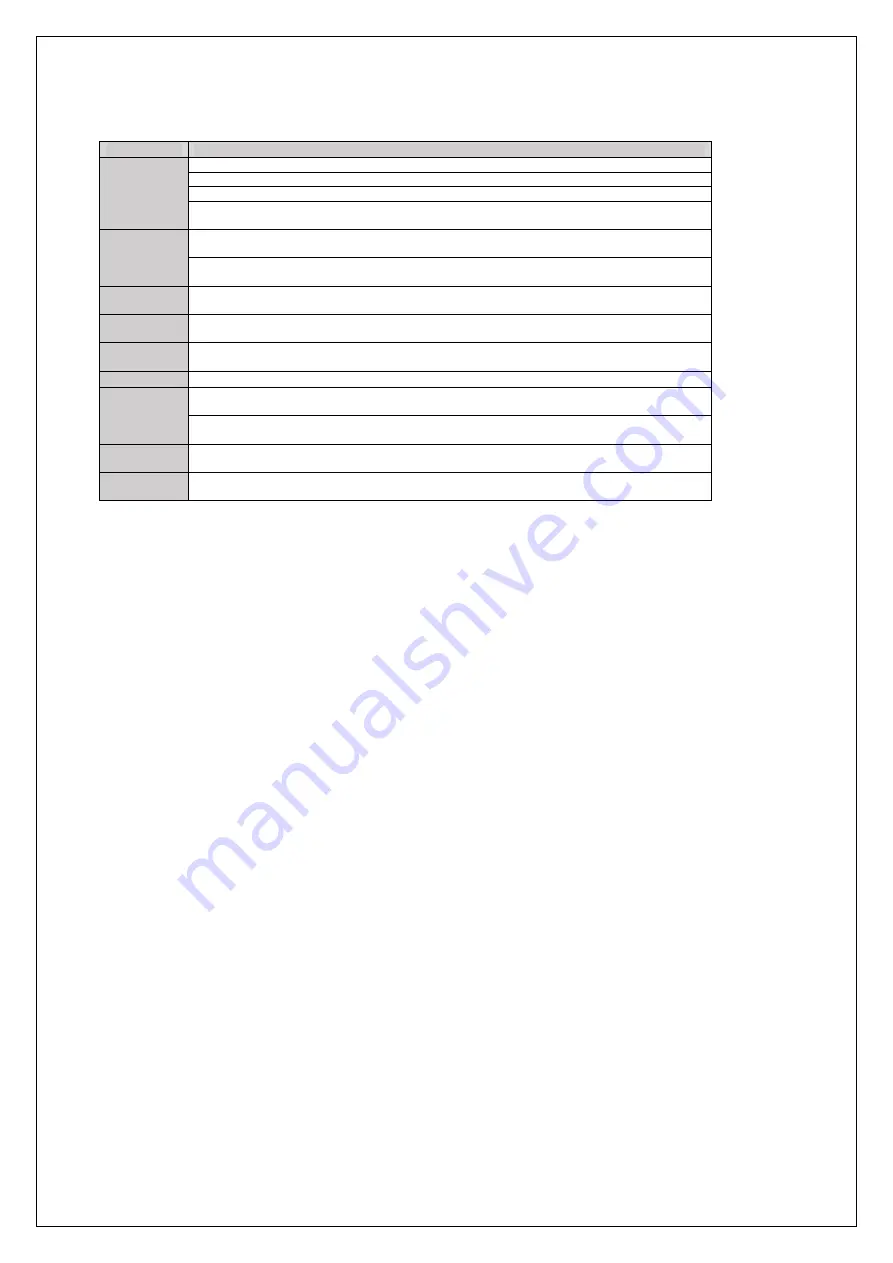
Table 3.1 Time Zones for Brake Sequence
Time Zone
Description
t1
Up or Down command is issued.
Safe Disable terminals H-HC must be set.
Speed reference must be selected by input terminals.
If the motor contactor feedback signal is not used, then the driver waits for the operation start delay time
set in S1-10 to pass, then it proceeds to the next step.
t2
After the delay time set in S1-10 has passed, the drive outputs current to the motor.
DC Injection Braking or Position Lock begins.
After the brake release delay time set in S1-06 has passed, the drive sets the “Brake Control” output in
order to release the brake.
t3
DC Injection Braking or Position Lock will continue until the time S1-04 has elapsed. Avoid setting S1-
06 greater than S1-04 since the motor could be driven against the applied brake.
t4
The drive accelerates up to the selected speed. The speed is kept constant until the leveling speed is
selected.
t5
Leveling speed is selected. The drive decelerates to the leveling speed and maintains that speed until the
Up or Down command is removed.
t6
The Up or Down signal is cleared. The drive decelerates to zero speed.
t7
The motor speed reaches the zero speed level (S1-01).
DC Injection Braking or Position Lock is then executed for the time set in S1-05.
After the delay time for closing the brake set in S1-07 has passed, the drive clears the “Brake Control”.
The brake applies.
t8
The drive continues DC Injection or Position Lock until the time set in S1-05 has passed. When S1-05
has passed, the drive output is shut off.
t9
After the delay for the magnetic contactor set in S1-11 has passed, the drive resets the output terminal set
for “Output Contactor Control”. The Safe Disable Inputs can be cleared and Baseblock can be enabled.
Step 5: Control Method Selection
The control method should be determined based on the requirements and available equipment. For
more landing accuracy, Open-loop control is recommended when PG is not available. If PG is used,
V/f with PG provides more accurate speed control.
Step 6: Motor parameters
If all motor parameters are available, E1 and E2 parameter groups should be set manually. E1-04, E1-
05, E2-01, E2-02, E2-03, E2-04, E2-05 are the necessary parameters for the normal operation of the
drive. If the resistance value of the motor is unknown, perform auto-tuning using the Auto-tuning
section of the panel. The auto-tuning procedure is explained in chapter 1. Note that the “output phase
loss” fault is based on the no-load current of the motor (E2-03), and if starting current is less than
25% of no-load current, the drive will trip and show “output phase loss” fault. To disable this fault,
the no-load current could be set zero.
Step 7: V/f Mode Selection
Determine which V/f curve is more suitable for the motor. Normal V/f curve is the most energy-
efficient method, however, the starting torque is not high enough to accelerate the motor. Using boost
manual curve with predefined values (E1-02=3) is highly recommended for elevator applications.
Torque boost option (E1-02=1) is an alternative option for motors with heavy loads. Experts can set
V/F curve manually using (E1-02=3 or E1=02=2) and E1-03. For more information, please refer to
E1: V/F pattern in chapter 2.
Step 8: Adjustments for Elevator Ride Comfort
This section explains the adjustment of drive settings used to eliminate problems with vibration and
rollback. Perform the steps presented in this section after the Basic Application Setup procedure is
completed.
The following table describes the most common problems encountered when riding an elevator with
an induction motor and propose the related solutions for these problems. Before taking any action,
make sure the startup procedures have been performed as previously described.
Содержание L450S
Страница 1: ...User Manual L450U L450S...
Страница 5: ...7 Figure 2 2 b SBT L450S I O block diagram...








































