Pr
o
Minent
®
Page 25
Commissioning
GUIDELINE
•
For gaseous chemicals there must be a continuous partial flow back to the supply
container. The return flow quantity should be approx. 20 % of the feed quantity.
•
The feed chemicals should be non-viscous and free from suspended particles.
•
The bypass tubing should end above the liquid level in the supply container. The
fine bleed valve then acts as a vacuum breaker which prevents the possibility of a
vacuum in the discharge tubing causing the container to be emptied.
Fine bleed function
When metering slightly gaseous chemicals the liquid end can be continuously de-aerated via the
fine bleed vent, if a coarse/fine bleed vent is present.
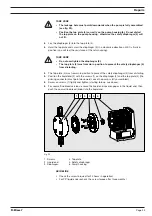
Open fine bleed vent (see fig. 23):
S
Pull off the cap (a) from the coarse/fine bleed vent (b).
S
Turn the screw (c) in the coarse/fine bleed vent approx. 1 turn anticlockwise with a
screwdriver.
c
a
1.
2.
b
Fig. 23
For self-bleed dosing pumps (SEK type):
GUIDELINE
On this liquid end the discharge connector is horizontal - the bleed valve is at the
top! (The bleed connector is identified on delivery with a red collar!)
S
Connect the suction and discharge tubing to the liquid end
S
Connect the bypass tubing to the liquid end
S
Switch on the gamma/ L and allow to run at maximum stroke length and stroke rate until the
liquid end is full and free from air bubbles (the feed chemical is visible in the bypass and
discharge tubing)
S
Switch off the gamma/ L
The gamma/ L is ready to operate.
8.1
Precision dosing settings
GUIDELINE
•
For highly viscous and gaseous chemicals select a large stroke length and a low
stroke rate!
•
For good mixing action, select a low stroke length and high stroke rate!
•
For precision dosing, set stroke length higher than 30 % (SEK type: higher than
50 %)!