46
COM6 is selected in Setup under COM5 Mode and COM6 Mode. For TTL, select
RS232/422.
One use of a TTL interface is for a TTL-level GPS module. AN RTCM SC-104
differential GPS module uses both COM ports. Some GPS modules only require one
port, in which case the other port could be configured for other serial interfaces.
COM5/6 as RS
–422 and RS–485 networks
COM5 and COM6 can also be used as RS–422 or RS–485. RS–422 and RS–485 use
differential signaling to communicate between the devices on a network.
Differential signal reduces the effect of environmental noise, allowing
communication over distances up to 1200 meters.
The RS–422 and RS–485 receivers provide an active high (space) condition for
shorted, open, or inactive lines. Note that RTS is used differently by RS–422 and
RS–485. Review the information in the following sections regarding RTS.
RS–422 is a point-to-point configuration. RS–485 is a multi-node configuration that
allows up to 32 nodes on a network. COM5 and COM6 can be configured in BIOS
Setup for RS–422 or RS–485. Refer to table 4–7 on page 45 for switch settings for
terminating an RS–422/485 network.
RS
–422
RS–422 is typically point to point configuration. RS–422 is also specified for multi-
drop (party-line) applications where only one driver is connected to, and transmits
on, a “bus” of up to 10 receivers. The device at the end of an RS–422 network must
be terminated. The XE–900 SBC optionally terminates with a 100 ohm resistor.
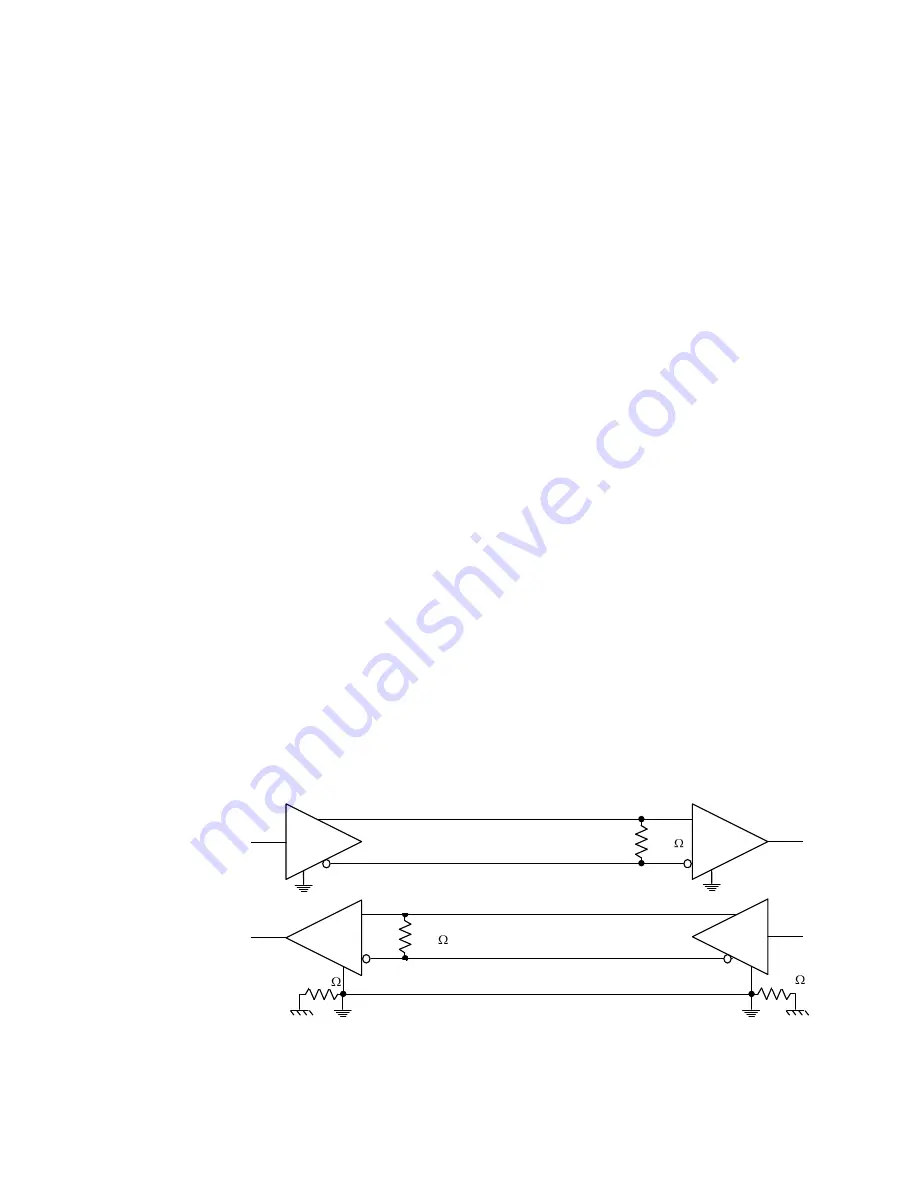
Refer to table 4–7. Figure 4–3 shows a typical RS–422 four-wire interface circuit.
The RTS* signal is used to control the transmitter and receiver in RS–422 mode.
The RTS* signal is controlled by the Modem Control Register bit 1 (MCR[1], which
is offset 0x04 from the UART base address). Writing MCR[1] to 0 (default state)
sets RTS* to an inactive state (RTS* = logic high) which ENABLES both the RS–
422 Transmitter and Receiver. Writing MCR[1] to 1 sets RTS* to an active state
(RTS* = logic low) which DISABLES both the RS–422 Transmitter and Receiver.
Figure 4–3
Typical RS–422 four-wire interface circuit
RS
–485
An application may implement a node as either the “host” node or as a “remote”
Receiver
Xmitter
100
100
TX –
RX +
TX +
RX –
Gnd
100
Receiver
Xmitter
100
RX –
TX +
TX –
RX +
Содержание XE-900
Страница 19: ...19 Figure 2 1 XE 900 SBC component diagram top ...
Страница 20: ...20 Figure 2 2 XE 900 SBC component diagram bottom ...
Страница 21: ...21 Figure 2 3 XE 900 SBC dimensions without Integrated Conductive Cooling System ...
Страница 38: ...38 ...
Страница 91: ...91 Figure 15 2 Dimensions for the Integrated Conductive Cooling System ...
















































