Disk Configuration
22
ReadyNAS for Home RAIDiator 5.3
Manage Disk Configuration
You can use Dashboard to manage the configuration of the hard disks installed in your
system.
Expand a Volume
Dashboard automatically manages volume expansion when you add a disk to your
ReadyNAS storage system. This expansion happens in the background while you continue to
use your ReadyNAS system. The volume expansion process can take several hours. If you
set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the expansion
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see
Alerts
on page
73.
Expand an X-RAID2 Volume
To expand your X-RAID2 volume, add a disk to your ReadyNAS storage system. The volume
is expanded in the background while you continue to use your storage system. For more
information about how to add a disk to your system, see the
ReadyNAS Duo v2 and NV+ v2
Hardware Manual
.
If you are adding a second disk, the new disk is used for data protection. If you are adding a
third or fourth disk, the new disk is used for additional storage capacity. For more information,
see
X-RAID2
on page
20.
Expand Flex-RAID Volumes
To expand your Flex-RAID volume or volumes, add a disk to your ReadyNAS storage
system. For more information about how to add a disk to your system, see the
ReadyNAS
Duo v2 and NV+ v2 Hardware Manual
.
The volume is expanded in the background while you continue to use your storage system.
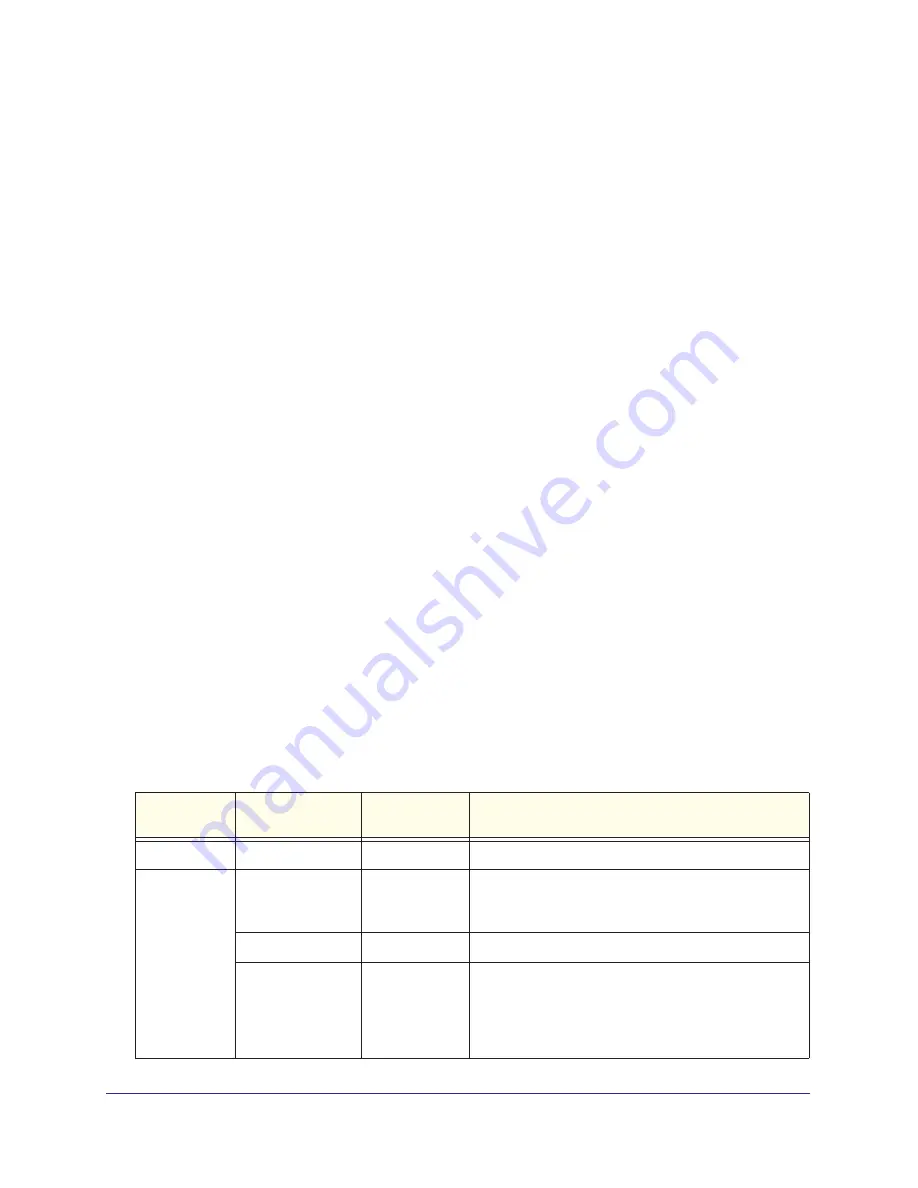
The following table describes how the ReadyNAS storage system handles expansion.
Table 2. Flex-RAID volume expansion behavior
Flex-RAID
format in use
Number of disks
currently installed
Number of
disks added
Volume expansion behavior
RAID 0
Any
Any
Another RAID 0 volume is created for each new disk.
RAID 1
2
1
Another RAID 1 volume is created made up of the new
disk. This volume has no data protection because RAID
1 requires two disks per volume to offer data protection.
2
2
Another RAID 1 volume is created.
3
1
The new disk is added to existing second volume; that
volume changes from an unmirrored state (because it
had only one disk) to a mirrored state. This means that
the fourth disk is used for data protection, not storage
capacity.