2202L5JE-DA-C5-N_2015.05.
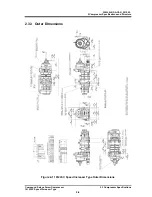
2 Compressor Specifications and Structure
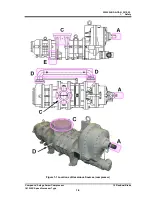
Compound 2-stage Screw Compressor
2.5 Mechanisms
1612LSC Speed Increaser Type
2-7
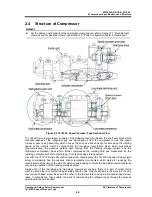
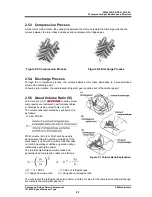
2.5.3 Compression
Process
As the rotors further rotate, the sealing line between them moves toward the discharge side and the
volume between the rotor lobes decreases and compresses the trapped gas.
Figure 2-5 Compression Process
Figure 2-6 Discharge Process
2.5.4 Discharge
Process
Through the compression process, the volume between rotor lobes decreases to a predetermined
value at the discharge port.
Following rotor rotation, the compressed refrigerant gas is pushed out of the discharge port.
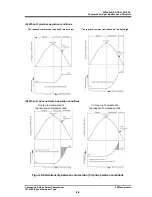
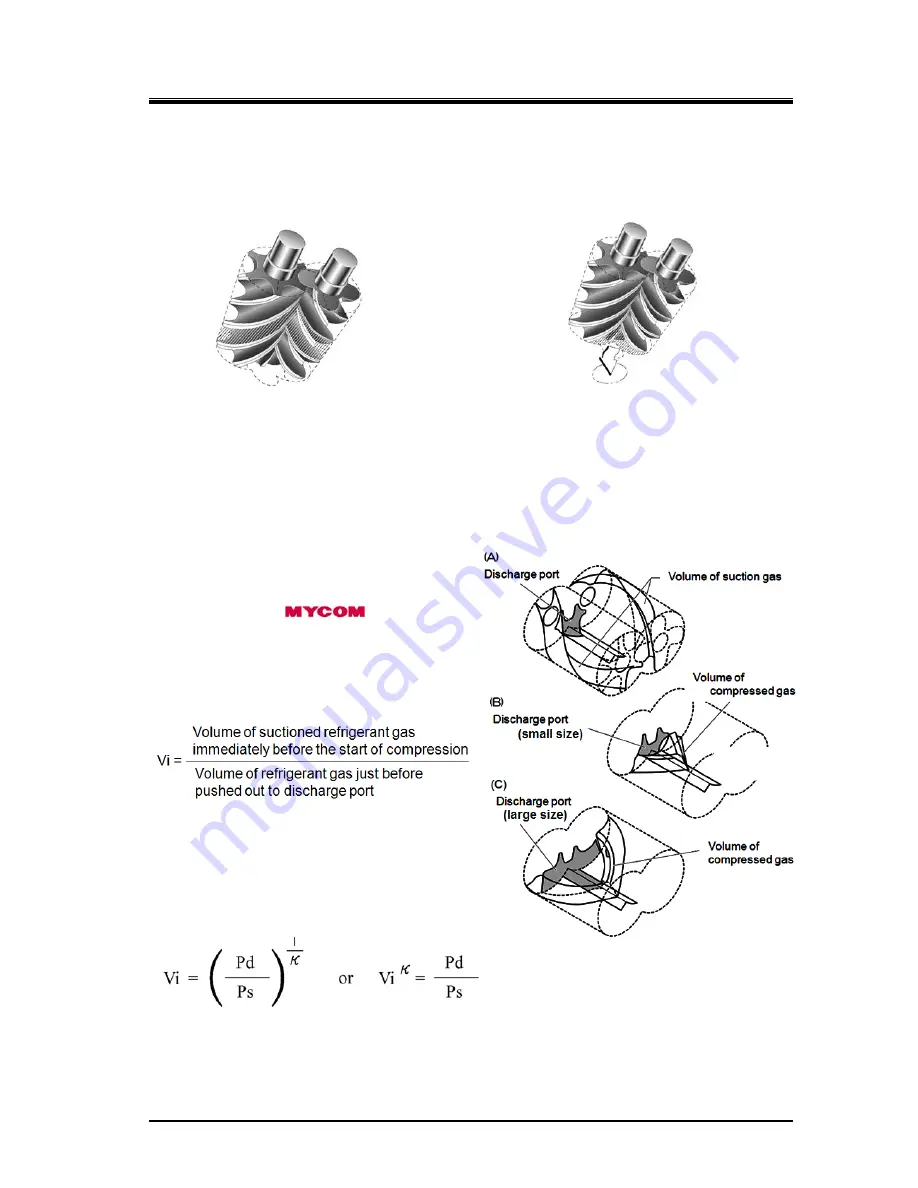
2.5.5 About Volume Ratio (Vi)
Volume ratios (Vi) of C-series screw
compressors are indicated in performance tables
or catalogs by using port symbols L and M.
The volume ratio represented by each symbol is
as follows:
L=2.63, M=3.65.
Which volume ratio (L or M) should be used is
decided according to operating conditions. If the
compressor is used with a volume ratio that does
not match operating conditions, operation will go
inefficiently wasting the power.
The relationship between volume ratios and
generally used compression ratios is as follows:
(Vi)
κ
=
π
i = Pd/Ps
κ
= Cp/Cv of refrigerant gas
Vi = designed volume ratio
π
i = designed compression ratio
The constant of the refrigerant gas also a factor, and the Vi value for the compression ratio will change
according to the refrigerant gas used.
Figure 2-7 Volume Ratio Explanation