3 Applications
This TFT LCD monitor in a metal housing is ide-
ally suited for applications in surveillance sys-
tems, but it can also be used for other purposes,
e. g. as a computer monitor or for multimedia
applications. The LED backlight of the screen
provides high colour brilliance and precise details
when reproducing pictures. For connecting the
signal sources the monitor is equipped with six
inputs (HDMI
TM
, DVI, VGA, S-Video and 2 ×
BNC). Feed-through outputs allow to pass on the
BNC input signals to further units. Additional
audio inputs and the integrated speaker also
allow for an audio reproduction. Via an on-screen
menu the monitor can exactly be adapted to the
respective application.
An IR remote control, a base, a power supply
unit, a VGA cable and an RCA cable are supplied
with the monitor.
4 Setting-up / Mounting
Set up the monitor via its base on an even and
stable surface. For better handling of the monitor
when connecting the units, the foot of the base
can be removed by pushing the PUSH button
and be replaced after connection. Incline the
monitor so that a favourable angle of view will
result. To prevent annoying reflections, it should
be placed so that light will not fall directly onto the
screen surface.
Instead of the base another monitor bracket
can be used which corresponds to the VESA-100
standard (e. g. the wall bracket MST-2 from
MONACOR). Unscrew the base and fix the
VESA bracket at the rear side of the monitor via
the four threaded holes arranged in a square.
5 Connections
5.1
Digital inputs
For digital connection of signal sources, the mon-
itor is equipped with an HDMI
TM
input (10) and a
DVI-D input (11). Via an HDMI
TM
connection
both video and audio data are transmitted, via a
DVI connection only video data are transmitted
(for audio reproduction use the 3.5 mm jack
“PC AUDIO IN”
chapter 5.2.2). If a digital out-
put is available at the signal source, this output
should take precedence as the digital connection
generally supplies a higher picture quality. Con-
nect the digital output to the corresponding input.
5.2
Analog inputs and outputs
5.2.1 Video
For analog video connection of a computer con-
nect the VGA output of the computer to the VGA
input “VGA IN” (12). A VGA connection cable is
supplied.
Resolution and picture frequency of the PC
graphics card must be adapted to the monitor.
The following combinations are compatible:
It is possible to connect the video outputs of two
signal sources which supply a composite video
signal, e. g. surveillance cameras, video recorders,
to the BNC inputs “VIDEO1 IN” and “VIDEO2 IN”
(14, 16).
It is possible to pass on the signals of the
inputs, e. g. to the video inputs of another moni-
tor or a recorder, via the BNC outputs “VIDEO1
OUT” and “VIDEO2 OUT” (15, 17): “VIDEO1
OUT” to feed through the signal at the input
“VIDEO1 IN” and “VIDEO2 OUT” to feed through
the signal at the input “VIDEO2 IN”. If an output is
not used, the corresponding input is automati-
cally terminated with 75 Ω.
A signal source which sends an S-Video signal,
e. g. digital recorder, may be connected to the
four-pole mini DIN input “Y/ C IN” (13).
5.2.2 Audio
To reproduce the sound of the signal sources at
the BNC inputs or the sound of the signal source
at the S-Video input, connect the audio outputs
of the sources to the respective RCA inputs
“AUDIO1 IN” and “AUDIO2 IN” (19, 21):
– the audio output of the source connected to
“VIDEO1 IN” (14) to the input “AUDIO1 IN”
– the audio output of the source connected to
“VIDEO2 IN” (16) or to “Y/ C IN” (13) to the
input “AUDIO2 IN”
Via the RCA outputs “AUDIO1 OUT” and
“AUDIO2 OUT” (18, 20) it is possible to pass on
the audio input signals to further units: “AUDIO1
OUT” to feed through the signal at the input
“AUDIO1 IN”, “AUDIO2 OUT” to feed through the
signal at the input “AUDIO2 IN”.
To reproduce the sound of the signal source at
the DVI input (11) or at the VGA input (12), con-
nect the audio output of the respective source to
the 3.5 mm jack “PC AUDIO IN” (22).
Note: The input “PC AUDIO IN” is designed as a stereo
jack, however, in case of a stereo connection only the
signal of the left channel is processed internally. To be
able to reproduce also the audio signal of the right chan-
nel, an adapter plug (stereo
→
mono) must be used.
5.3
Power supply
Connect the power supply unit provided to the
jack “DC12V IN” (8) and connect it to a mains
socket (230 V~ / 50 Hz) via the mains cable pro-
vided. When connected to the socket, the power
supply unit is in operation, its power LED will light
up.
The monitor is switched on as soon as it is con-
nected to the power supply via the power supply
unit (
chapter 7).
6 Remote control
The infrared remote control provided is supplied
with a battery. Prior to the first setting into opera-
tion, remove the foil at the battery support. When
actuating the remote control, always direct it
towards the IR sensor (2) of the monitor. There
must be no obstacles between sensor and
remote control.
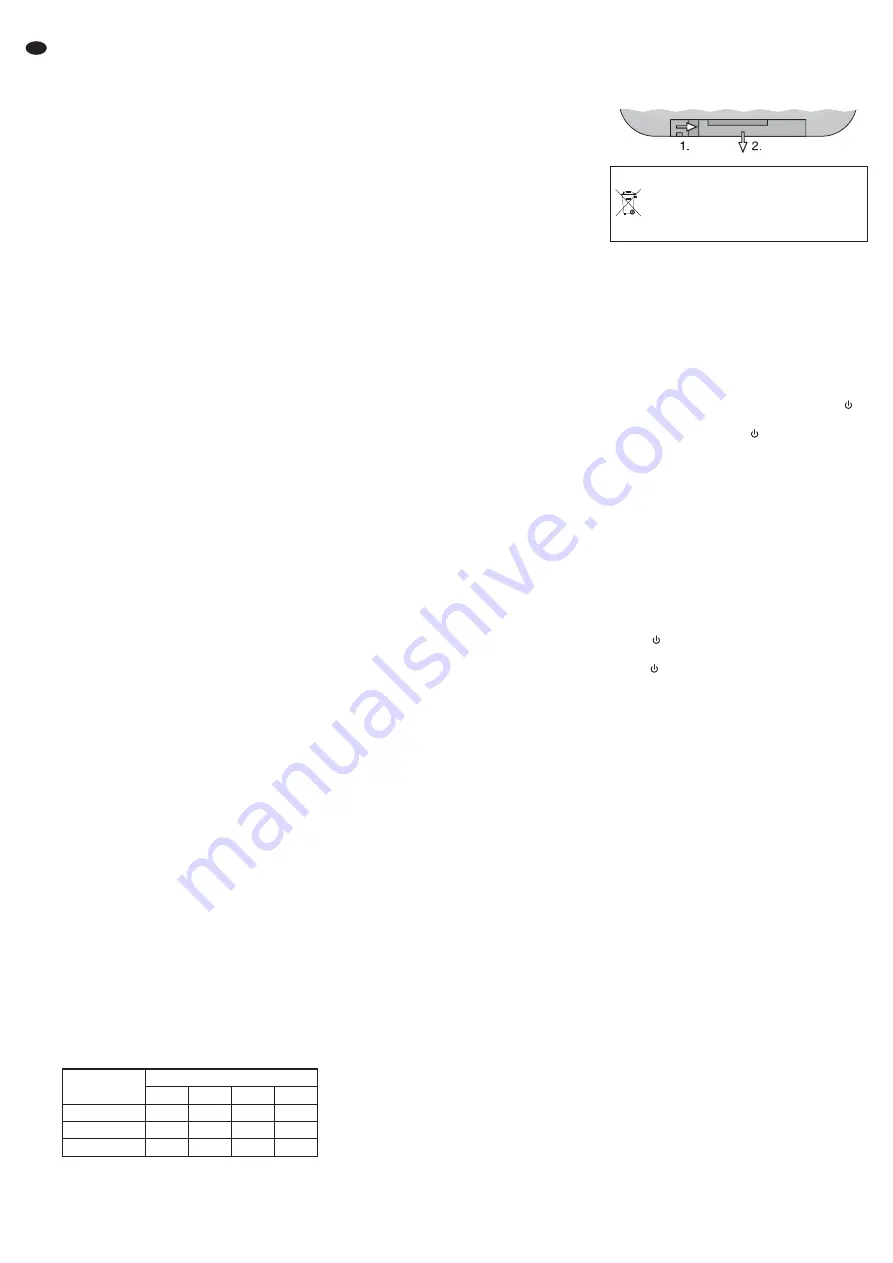
To replace an exhausted battery, push the
locking of the battery support to the right (1st
arrow in the figure below) and remove the sup-
port (2nd arrow). Remove the exhausted battery.
Insert a 3 V button cell of type CR 2025 with the
positive pole showing upwards into the support
and slide it in again.
If the remote control is not used for a longer
period, the battery should be removed for safety
reasons. Thus, the remote control will not be
damaged in case the battery should leak.
7 Setting into Operation
After connection of the power supply, the monitor
is switched on and reproduces pictures and
sound of the last signal source selected. The
power LED (1) shows green. It is possible to
indicate the source concerned with the button
“Display” (35) or the button
(6) on the monitor
(
chapter 8.1).
To change to stand-by, press the button
(7
or 29), the power LED will extinguish. To switch
on, press again the button
on the monitor or on
the remote control.
With the video signal missing / video loss:
If the monitor is switched on and does not receive
any video signal from the selected source, the
screen remains blue for 30 seconds, then the
monitor is switched to stand-by and the power
LED (1) is changed to red. With missing video
signal, there will also be no audio reproduction of
the source. The monitor is switched on again as
soon as the source supplies a video signal to the
monitor.
To be able to change to another source in
case the video signal is missing, first press the
button
to terminate the video loss status
(power LED will be extinguished), then press the
button
once more to switch on the monitor
again. Then select another source within 30 sec-
onds (
chapter 8.2).
Note: The monitor has a low power consumption even
in stand-by mode. To switch off monitor and power sup-
ply unit completely when the units are not in use for a
longer period of time, disconnect the power supply unit
from the mains socket in order to save energy.
8 Operation
This chapter includes all adjustments which can
be made without calling the on-screen menu
(adjustments in the on-screen menu
chapter 9).
8.1
Showing the name of the source
and short information
When the arrow key
(6) on the monitor or the
button “Display” (35) is pressed, on the top right
of the picture the following information is shown
for a few seconds:
– the name of the selected source:
AV 1
= source at the input “VIDEO1 IN” (14)
AV 2
= source at the input “VIDEO2 IN” (16)
S-Video
= source at the input “Y/ C IN” (13)
PC
= source at the VGA input (12)
DVI
= source at the DVI input (11)
HD
= source at the HDMI
TM
input (10)
– short information about the source, e. g. video
standard PAL or NTSC for sources at the BNC
inputs or resolution and picture frequency for a
computer at the VGA input.
Do not put exhausted batteries into the
household rubbish but take them to a
special waste disposal (e. g. collective
container at your retailer) to protect the
environment.
Resolution
Picture frequency
60 Hz
70 Hz
72 Hz
75 Hz
800 × 600
√
√
√
1024 × 768
√
√
√
1280 × 1024
√
√
10
GB

























