< Dual-In-Line Package Intelligent Power Module >
Series Application note
Publication Date: September 2016
43
3.2.2 performance according to carreir frequency
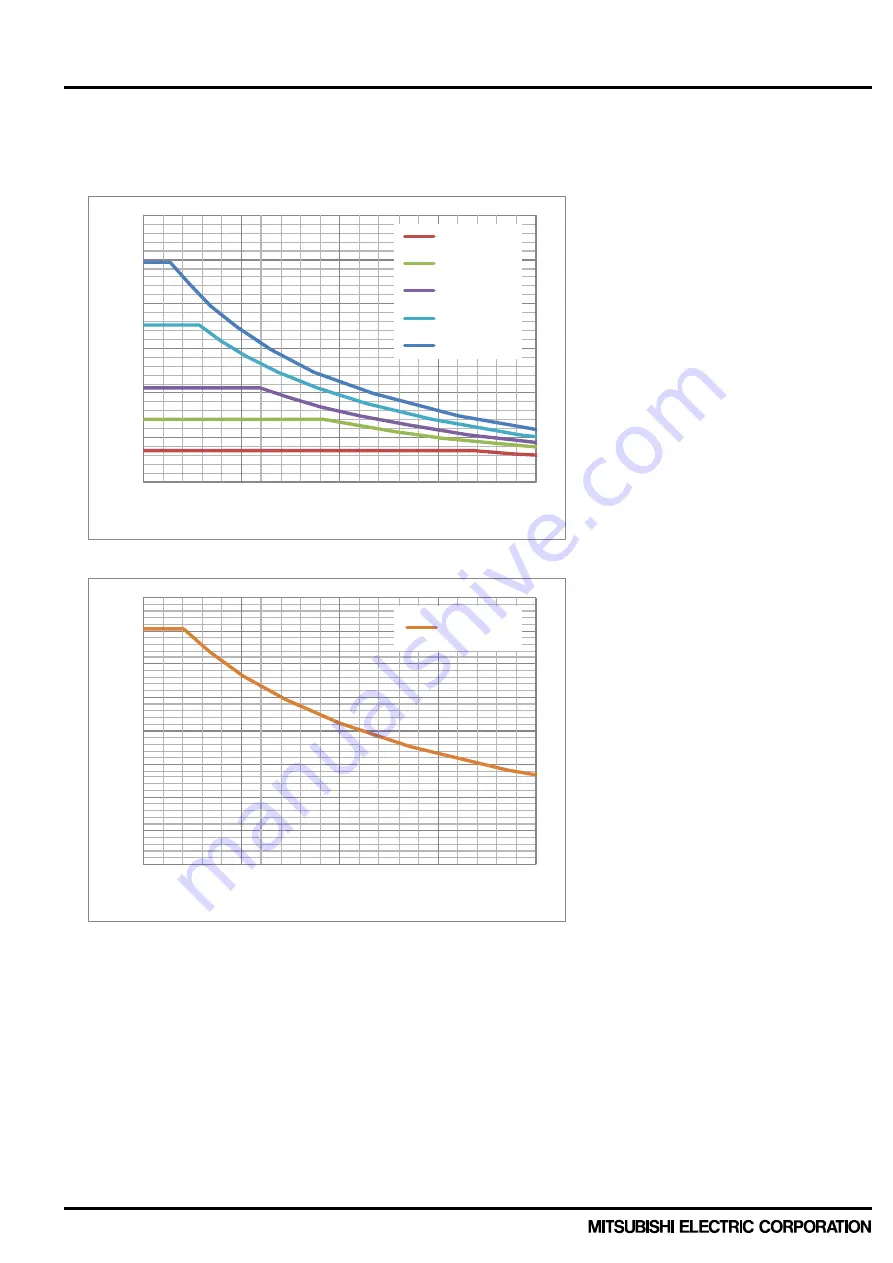
Fig.3-2-2 shows the typical characteristics of allowable effective current vs. carrier frequency under the following
inverter operating conditions based on power loss simulation results for 1200V series. And Fig.3-2-3
shows for PSS50xC1F6.
Fig.3-2-2 Effective current-carrier frequency characteristics
Fig.3-2-3 Effective current-carrier frequency characteristics
Fig.3-2-2 and Fig.3-2-3 show one of the example of estimating allowable inverter output effective current with
different carrier frequency and allowable maximum operating temperature condition (T
c
=100°C. T
j
=125°C). The
results may change for different control strategy and motor types. Anyway please ensure that there is no large
current over device rating flowing continuously.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0
5
10
15
20
Allo
w
ab
le
cu
rr
en
t [
Ar
m
s]
Career Frequency [kHz]
PSS05xC1FT
PSS10xC1FT
PSS15xC1FT
PSS25xC1FT
PSS35xC1FT
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0
5
10
15
20
Allo
w
ab
le
cu
rr
en
t [
Ar
m
s]
Career Frequency [kHz]
PSS50xC1F6
[Calculation condition for PSSxxxC1FT]
V
CC
=600V, V
D
=V
DB
=15V,
V
CE(sat)
=Typ., Switching loss=Typ.,
T
j
=125°C, T
c
=100°C,
ΔT
j-c
=25K
R
th(j-c)
=Max.
P.F=0.8, 3-phase PWM modulation,
60Hz sine waveform output
[Calculation condition for PSS50xC1F6]
V
CC
=300V, V
D
=V
DB
=15V,
V
CE(sat)
=Typ., Switching loss=Typ.,
T
j
=125°C, T
c
=100°C,
ΔT
j-c
=25K
R
th(j-c)
=Max.
P.F=0.8, 3-phase PWM modulation,
60Hz sine waveform output
Carrier Frequency [kHz]
Carrier Frequency [kHz]













































