© 2017 Sensata Technologies
44
Appendix B – Battery Information
B-1 Battery
Information
Battery Bank Sizing
The size of the battery bank determines how long the inverter can
power the AC loads without recharging. The larger the battery bank,
the longer the run time. Size your battery bank to the system’s AC
load requirements and the length of time required to run the load from
the batteries. In general, the battery bank should not be discharged
more than 50%.
Battery Types
Batteries are available in different sizes, amp-hour ratings, voltage,
and chemistries; they also come in liquid or gel, vented or non-
vented, etc. They are also available for starting applications (such
as an automobile starting battery) and deep discharge applications.
Only the deep cycle types are recommended for inverter applications.
Choose the batteries best suited for the inverter installation and cost.
Use only the same battery type for all batteries in the bank. For best
performance, all batteries should be from the same lot and date.
This information is usually printed on a label located on the battery.
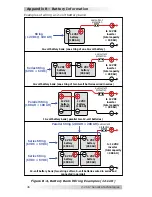
Battery Confi guration
The battery bank must be wired to match the inverter’s DC input
voltage speci
fi
cations. In addition, the batteries can be wired to
provide additional run time. The various wiring con
fi
gurations are:
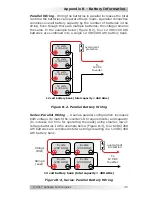
Series Wiring
– Wiring batteries in a series increases the total battery
bank output voltage. A series connection combines each battery in a
string until the voltage matches the inverter’s DC requirement. Even
though there are multiple batteries, the capacity remains the same.
In the example below (Figure B-1), two 6 VDC/200 AHr batteries are
combined into a single string—resulting in a 12 VDC/200 AHr bank.
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
overcurrent protection
12 volt battery bank (total capacity = 200 AHrs)
To
12 VDC
Inverter
Figure B-1, Series Battery Wiring