© 2017 Sensata Technologies
14
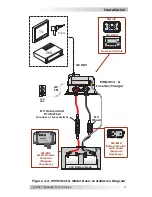
Installation
2.2
DC Wiring
This section describes the MMS Series inverter’s required DC wire
sizes, the recommended disconnect/overcurrent protection, and how
to make the DC connections to the inverter and the battery bank.
2.2.1 DC Wire Sizing
It is important to use the correct DC wire to achieve maximum
ef
fi
ciency from the system and to reduce
fi
re hazards associated with
overheating. Use Table 2-1 to select the minimum DC wire size needed
based on your inverter model. If the distance from the inverter to
the battery bank is greater than 5 feet (152.4 cm), use the bottom
part of that table to help determine the minimum recommended
cable sizes for longer distances. Always keep your wire runs as short
as practical to help prevent low voltage shutdowns and to keep the
DC breaker from nuisance tripping (or open fuses/circuit breakers)
because of increased current draw. Undersized cables can also lower
the inverter’s peak output voltage, as well as reduce its ability to
surge heavy loads.
Info:
The DC wires must be color coded with colored
tape or heat shrink tubing; RED for positive (+), BLACK
for negative (–), and GREEN for DC ground.
The DC wires must have soldered and crimped lugs, crimped copper
compression lugs, or aluminum mechanical lugs. Soldered connections
alone are not acceptable for this application.
If the inverter is expected to operate at a distance greater than 5 feet
(152.4 cm) from the battery bank, the DC wire size will need to be
increased to overcome the increase in resistance—which affects the
performance of the inverter. Continue to use the overcurrent device
and DC ground wire previously determined from Table 2-1 and then,
refer to the bottom part of that table to determine the minimum DC
wire size you need for various distances based on your inverter model.
2.2.2 DC Overcurrent Protection
For safety and to comply with NEC (National Electrical Code) electrical
code regulations, you must install a DC overcurrent protection
device in the positive DC cable line to protect your DC cables. This
DC overcurrent device can be a fuse or a circuit-breaker, but must
be DC rated. It must be correctly sized according to the size of DC
cables being used, which means it is required to open before the cable
reaches its maximum current carrying capability, thereby preventing
a
fi
re.
See Table 2-1 to select the DC overcurrent device based on
the minimum wire size for your inverter model.