Triton Go Product Manual |
Wiring and Connections
INGENIA | 05/29/2017
97
77
http://doc.ingeniamc.com/display/EMCL/Sources
78
http://doc.ingeniamc.com/display/EMCL/ReManual
79
http://ingeniamc.com/software#motionlab
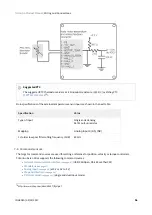
•
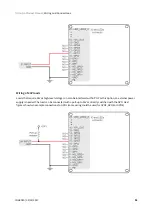
Encoder follower / electronic gearing
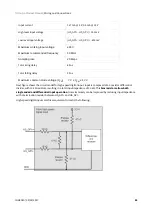
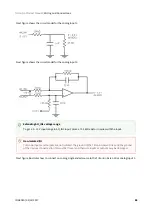
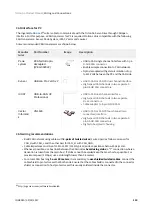
Analog inputs, step and direction, PWM command and encoder follower / electronic gearing are interfaced
through general purpose inputs. Next table illustrates which variables can be controlled with each command
source:
Command source
Target variable
Network interface
Position, velocity, torque
Standalone
Position, velocity, torque
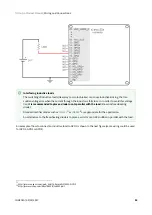
Analog input (+/- 10 V o 0 – 5 V)
Position, velocity, torque
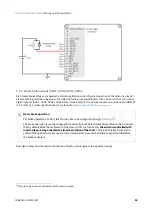
Step and direction
Position
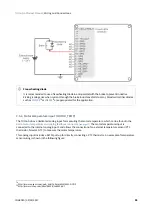
PWM command
Position, velocity, torque
Encoder following / electronic gearing
Position
Please, see
documentation for configuration details.
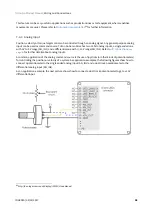
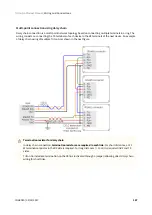
7.6.1 Network communication interface
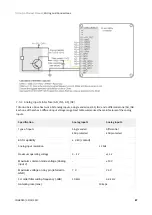
Triton Go Servo Drive can utilize network communication as a form of input command. Supported network
interfaces for Triton Go Servo drive are CAN (CANopen protocol), USB, RS-485 and EtherCAT.
USB interface is not suitable for long distances or noisy environments. This protocol is only recommended for
configuration purposes.
For normal operation, it is suggested to use CAN, RS-485 or EtherCAT. These interfaces are more robust against
noise than USB, and allow higher distances between the Triton Go Servo Drive and the commander. These
command sources can be used for setting position, velocity or torque target.
For further information, see
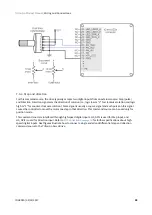
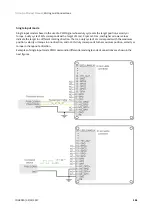
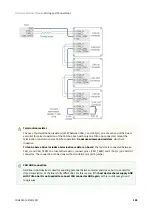
7.6.2 Standalone
Triton Go Servo Drive is provided with an internal non-volatile memory where a standalone program can be
saved. With the use of Ingenia
suite, the user can configure and save instructions to this 1 Mb
(128K x 8bit) EEPROM, allowing Triton Go Servo Drive to work in standalone mode. In this mode, there is no
need of any external command source.
Programs or macros composed with Motion Lab suite allow to
configure position, velocity or torque
targets
and to
interface with general purpose inputs and outputs.