WIRELESS
Version 1.0, 02/2015. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
77
Version 1.0, 02/2015. Copyright 2014 Hitron Technologies
77
Hitron CGNVM User’s Guide
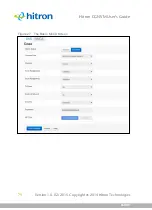
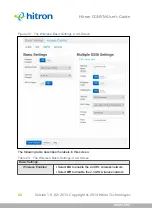
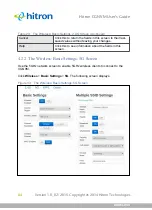
4.1.5
Wireless Security
Radio is inherently an insecure medium, since it can be intercepted by anybody in the
coverage area with a radio receiver. Therefore, a variety of techniques exist to control
authentication (identifying who should be allowed to join the network) and encryption
(signal scrambling so that only authenticated users can decode the transmitted data).
The sophistication of each security method varies, as does its effectiveness. The
CGNVM supports the following wireless security protocols (in order of effectiveness):
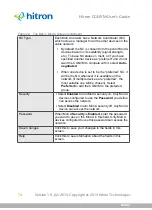
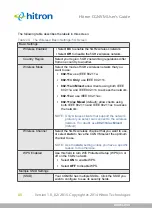
WEP
(the Wired Equivalency Protocol): this protocol uses a series of “keys” or
data strings to authenticate the wireless client with the AP, and to encrypt data
sent over the wireless link. WEP is a deprecated protocol, and should only be
used when it is the only security standard supported by the wireless clients.
WEP provides only a nominal level of security, since widely-available software
exists that can break it in a matter of minutes. Additionally, use of WEP limits the
wireless network speed to a speed of 54MBps (802.11g speed).
WPA-PSK
(WiFi Protected Access - Pre-Shared Key): WPA was created to
solve the inadequacies of WEP. There are two types of WPA: the “enterprise”
version (known simply as WPA) requires the use of a central authentication
database server, whereas the “personal” version (supported by the CGNVM)
allows users to authenticate using a “pre-shared key” or password instead.
While WPA provides good security, it is still vulnerable to “brute force”
password-guessing attempts (in which an attacker simply barrages the AP with
join requests using different passwords), so for optimal security it is advised that
you use a random password of thirteen characters or more, containing no
“dictionary” words.
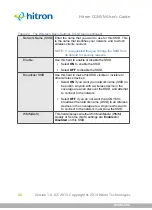
WPA2-PSK
: WPA2 is an improvement on WPA. The primary difference is that
WPA uses the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) encryption standard
(which has been shown to have certain possible weaknesses), whereas WPA2
uses the stronger Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode
with Cipher block chaining Message authentication code Protocol (CCMP),
which has received the US government’s seal of approval for communications
up to the Top Secret security level. Since WPA2-PSK uses the same pre-shared
key mechanism as WPA-PSK, the same caveat against using insecure or
simple passwords applies.
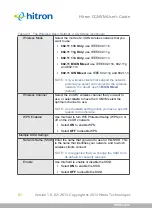
NOTE:
The CGNVM can be configured to use the TKIP encryption standard;
however, this limits the wireless network speed to 54Mbps (802.11g speed).