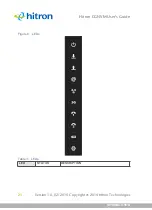
STATUS
Version 1.0, 02/2015. Copyright 2012 Hitron Technologies
31
Version 1.0, 02/2015. Copyright 2014 Hitron Technologies
31
Hitron CGNVM User’s Guide
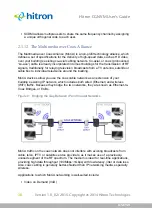
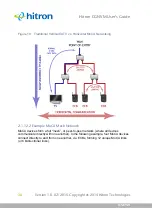
The private network is your Local Area Network (LAN) and Wireless Local Area
Network (WLAN), if enabled. You are free to assign IP addresses to computers
on the LAN and WLAN manually, or to allow the CGNVM to assign them
automatically via DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). IANA has
reserved the following blocks of IP addresses to be used for private networks
only:
If you assign addresses manually, they must be within the CGNVM’s LAN
subnet.
2.1.2.3
Subnets
A subnet (short for sub-network) is, as the name suggests, a separate section of a
network, distinct from the main network of which it is a part. A subnet may contain all
of the computers at one corporate local office, for example, while the main network
includes several offices.
In order to define the extent of a subnet, and to differentiate it from the main network,
a subnet mask is used. This “masks” the part of the IP address that refers to the main
network, leaving the part of the IP address that refers to the sub-network.
Each subnet mask has 32 bits (binary digits), as does each IP address:
A binary value of
1
in the subnet mask indicates that the corresponding bit in the
IP address is part of the main network.
A binary value of
0
in the subnet mask indicates that the corresponding bit in the
IP address is part of the sub-network.
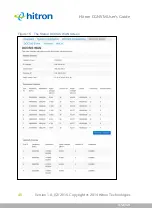
For example, the following table shows the IP address of a computer (
192.168.1.1
)
expressed in decimal and binary (each cell in the table indicates one octet):
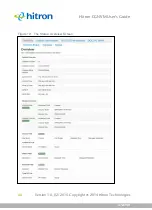
Table 5:
Private IP Address Ranges
FROM...
...TO
10.0.0.0
10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0
172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0
192.168.255.255
Table 6:
IP Address: Decimal and Binary
192
168
0
1
11000000
10101000
00000000
00000001