- 49 -
GPS
For centuries, sailors haven en searching for a reliable and precise method of travelling the world’s
waterways. From celestial navigating to the modern navigation techniques as Loran, Decca navigator,
Omega or Transit Satnav, each system has had its problems with weather, range and reliability.
Without doubt, the “Global Positioning System”, or GPS for short, is the most significant advance in
navigation: it fives the navigator a position 24 hours a day, 365 days a year in any weather condition.
GPS is a satellite based navigation system which provides suitably equipped users with accurate
position, velocity and time data. Originally the GPS, developed by the U.S. Department of Defense,
was conceived for military purposes, but now it is used in a host of civilian applications.
GPS navigation uses satellite signals to determine your position in relation to a set of satellites orbiting
the earth. The GPS constellation of satellites continuously send radio signals, containing the precise
position for each satellite back to earth. By knowing the position of 3 or 4 satellites and calculating
various time differences between transmitted signals, the GPS receiver can determine its present
position anywhere on earth, and thanks to continuous updates, calculate speed and course
information.
HOW GPS WORKS
Currently, the GPS constellation consists of 26 orbiting satellites (including 3 spares), but this number
will increase in the future.
The GPS receiver computes an accurate position by calculating the distance to the GPS satellites that
orbit the earth. Signals are required from 3 satellites for two dimensional (2D) position calculation
whilst 4 satellites are required for three dimensional (3D) position calculation.
As mentioned earlier, GPS satellites are not geostationary, but they are orbiting the earth as illustrated
on the following figure:
[The GPS constellation]
Note that position is repeatedly fixed through the following three steps while any 3 satellites are in line
of sight.
The position calculation procedure is indicated in the following three steps:
1. GPS satellites continuously transmit their own precise orbital data and the GPS receiver
computes their locations by receiving this data.
2. In this receiving process, the GPS receiver measures very accurate distances to the satellites,
using
Содержание HIS-70R
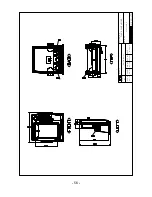
Страница 12: ... 12 HIS 70R System HIS 70R Metal Front Rear Main Screen Keypad Knob Mounting Bracket Connector ...
Страница 13: ... 13 HIS 70R System HIS 70R Plastic Front Rear Main Screen Keypad Knob Mounting Bracket Connector ...
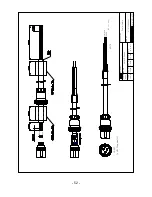
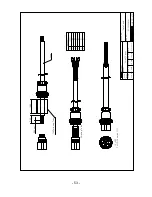
Страница 14: ... 14 HIS 70R System SPEC of the connectors Metal Plastic ...