Theory of Operation
2097937-002 Rev G
T2100-ST1 Treadmill, 110V / T2100-ST2 Treadmill, 220V
67
11 March 2019
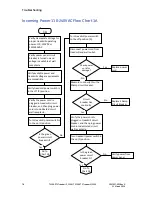
Smart Power Supply (PCB) Overview
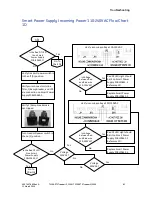
When power is applied to the unit, the UPS reads the contents of
the non-volatile memory and verifies the calibration contents
with a checksum. If the contents are not valid, the calibration
constants are set to non-operational values and the unit is put
into a state where operation is suspended pending recalibration.
If the contents are valid, the unit enters a startup mode where
the system checks to see if it should enter self-test mode
(described in the “Self-Test Mode” on page 70) and begins to find
the zero elevation point by turning on the elevation motor in the
down direction. If motion is not detected for two seconds, the
system assumes that the lower elevation limit has been reached.
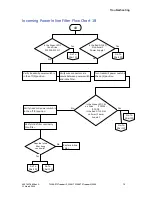
During the “elevation zeroing” time, if a command to start the
belt is received from the PC, it is assumed that the PC is not
aware of the UPS power cycle and the unit will enter a non-
responsive state (waiting for either a communication timeout or
a stop command). If the elevation limit is found without receiving
a start belt command, the UPS enters the operational mode with
a set speed and set elevation of zero.
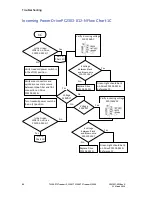
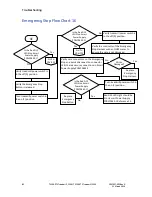
In operational mode, the unit continuously controls the belt
speed output, the belt-enable output, and the outputs to raise or
lower the elevation based on the current set points for speed and
elevation. Through the use of either communication port, the
unit accepts commands to modify the belt state, the belt speed,
and the deck elevation. The current state of the control may also
be queried through the use of this serial port. As commands are
received to change the set point speed or set point grade, they
are checked for format and range. Pending approval, the new set
points are adopted and adjustments are made to the state of the
outputs.
Speed control is done in a closed loop that monitors the belt
speed using two different speed references. The first is a
magnetic reed switch located on the motor side of the belt
pulley, and the second is a speed reference supplied by the
motor controller. A speed calibration is required to provide a
target speed output for a given set point. After the initial target
is reached, the speed inputs are constantly monitored to make
adjustments to the speed output and to detect over speed, zero
speed, or speed sensor comparison fault conditions. In the case
of a fault condition, the belt is stopped and operation is
suspended.
Elevation position control is done using relays to turn on the
elevation motor in the up or down direction depending on the
current set point. A micro-switch input is used to determine the
position of the elevation motor by counting revolutions of the
elevation motor’s internal gearing. An elevation calibration is
required to provide an accurate number of counts from zero to