CMSX-...-C-U-F1-...
Festo – CMSX-...-C-U-F1-... – 1506a English
9
3.1
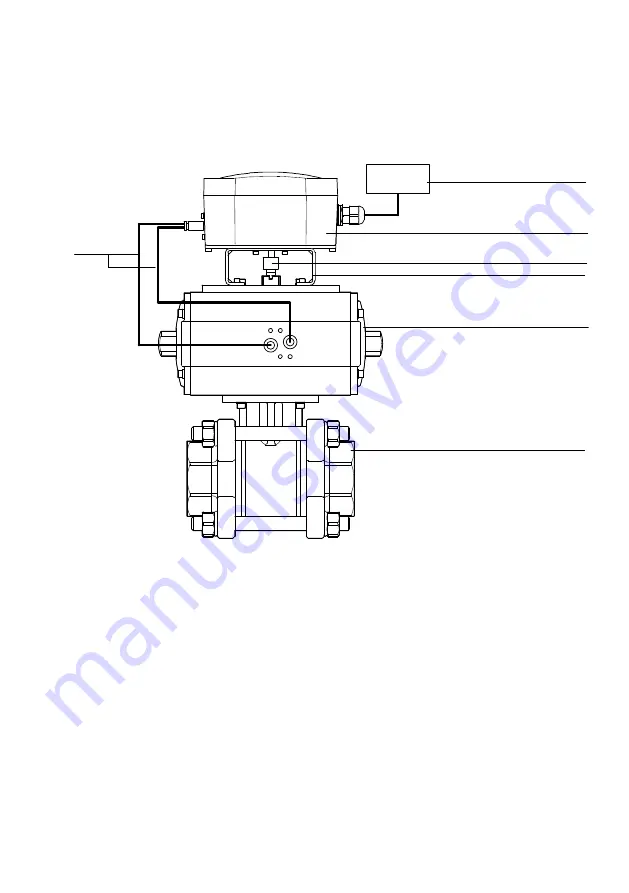
System structure
The following figure shows the basic system structure of a process valve unit, comprising a CMSX posi
tioner and a semi-rotary drive with process valve.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
Higher-order system (PLC/IPC or external
setpoint generator)
2
CMSX positioner
3
Mechanical coupling
4
Mounting adapter – example
5
Semi-rotary drive – example (here DFPB)
6
Process valve – example (here VZBA)
7
Air – port 2 and 4
Fig. 5
System structure with semi-rotary drive (example)
Positions are specified through an analogue setpoint signal via a master PLC/IPC or manually on-site
via an external setpoint generator (
è
The positioner with potentiometer and fast-switching valves (
è
with process valve (
è
) are connected to each other in such a way that a closed control
circuit results. In this control circuit, the position of the drive represents the controlled variable. The
potentiometer registers permanently the position of the drive (actual value of the controlled variable)
and transmits this to the controller as an electric signal. It compares the analogue specified setpoint
position (reference variable) to the current position and calculates from this the positioning signals
(manipulated variable – pulse-width modulation) for the fast-switching valves. The fast-switching
valves control the drive by pressurizing and venting the cylinder chambers.










































