Required measures
Measures
Description
Line choke
(2 x
³
5 mH)
A line choke with two partial windings for the line feeds L1 and N (2 x
³
5 mH)
must be installed to comply with the mains harmonics in accordance with
EN 61000-3-2 – accessories.
Snap ferrite
A snap ferrite (Würth, prod. no. 74272722 or compatible) on motor phases U, V,
W (without PE) must be installed to comply with the malfunction limit values of
category C2 at a switching frequency of 16 kHz. Feed through flying leads once.
external mains
filter
Install a suitable external mains filter – Accessories.
Tab. 15: Installation measures to achieve the specified category
For installation of a line choke and a snap ferrite
–
If set-up and commissioning are performed by a professional with the neces-
sary experience for setting up and commissioning drive systems, including
their EMC aspects, category C2 devices can be used in the first environment
(residential area).
–
For operation of category C2 devices, limit values for the harmonic currents
in the network (EN 61000-3-2 or EN 61000-3-12) apply, depending on the
connected load of the machine. Please check whether this is the case for
your facility/system. As a rule, compliance with the limit values for harmonic
currents requires the use of external filter measures, e.g. installation of a line
choke.
–
For operation of category C2 devices, limit values for the harmonic currents
in the network (EN 61000-3-2 or EN 61000-3-12) apply, depending on the
connected load of the machine. Please check whether this is the case for your
facility/system.
–
Category C3 devices are intended for use in the second environment only
(industrial environment). Use in the first environment is not permitted.
This product can generate high frequency interference, which may make it neces-
sary to implement interference suppression measures in residential areas.
In practice, the combination of the components used and their properties influ-
ence the achievable length of the motor cable
è
Manual Assembly, Installation.
7.7
Connection examples
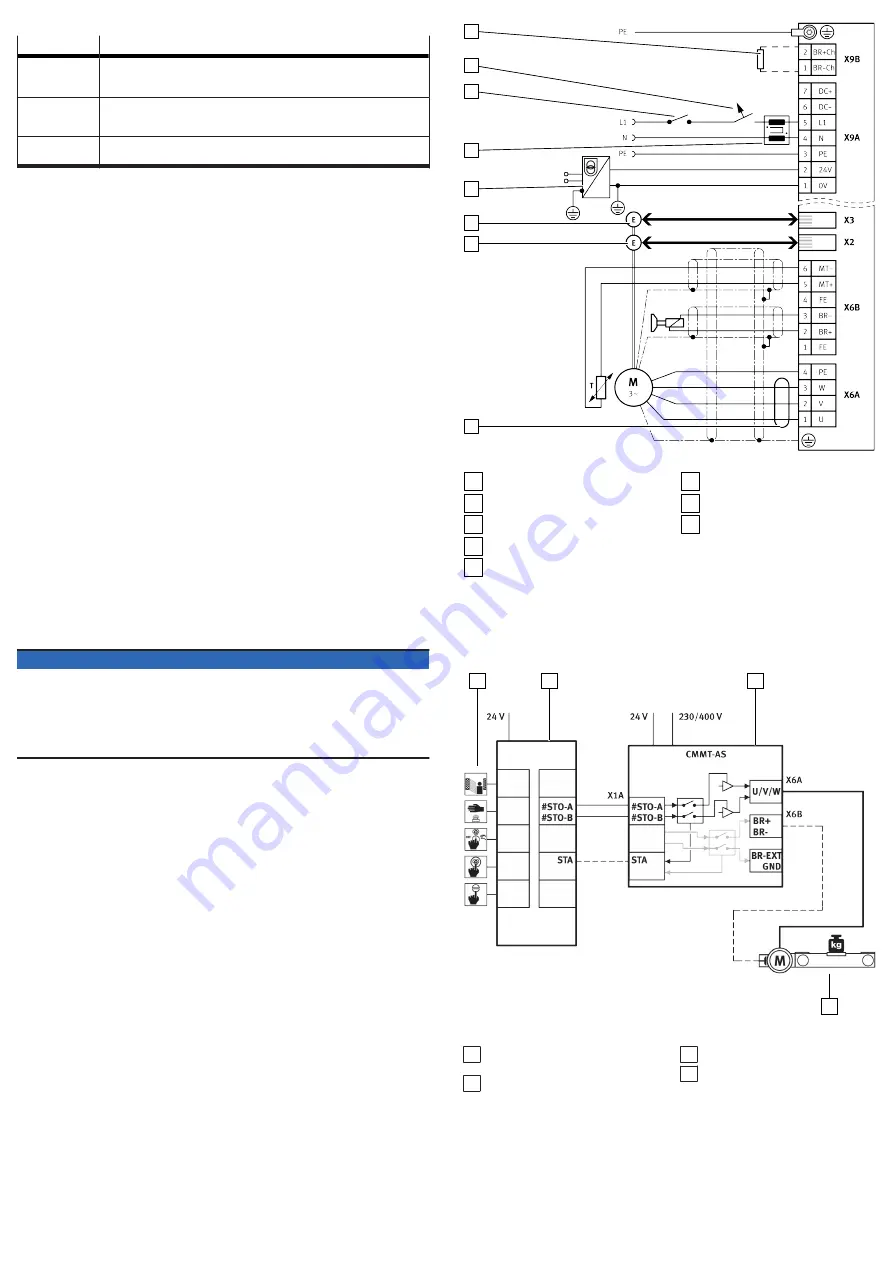
Connection plan, 1-phase mains connection
The following connection diagram shows the 1-phase mains connection of the
device with fuse and main switch that does not interrupt the neutral conductor
(uninterrupted connection of the neutral conductor when switching on and off).
This type of connection is required if several 1-phase powered servo drives with
a common neutral conductor reference are distributed to the mains phases L1, L2
and L3 in a network.
If otherwise stipulated that the neutral conductor must be disconnected when
switching on and off, the following note must be observed:
NOTICE
Overvoltage due to asymmetrical mains load
If the neutral conductor has to be disconnected when the device is switched
on and off, the device can be damaged by overvoltage due to an asymmetrical
network load.
• Design the mains connection with fuse and main switch so that the neutral
conductor is always switched on early and switched off later.
1
4
2
3
5
6
7
8
Fig. 6: Connection example, 1-phase mains connection
1
Braking resistor
2
Circuit breaker or fuse
3
Main switch/main contactor
4
Line choke (for category C2)
5
PELV fixed power supply for 24 V
supply
6
Encoder 2 (optional)
7
Encoder 1
8
Snap ferrite (for category C2,
16 kHz)
Measures for 2-phase mains connection
è
Manual Assembly, Installation.
STO connection example
The safety sub-function STO (safe torque off) is triggered by an input device that
makes the safety request (e.g. light curtain).
1
2
3
4
Fig. 7: STO sample circuit
1 Input device for safety request
(e.g. light curtain)
2 Safety relay unit
3 Servo drive CMMT-AS
4 Drive axle
Information on the sample circuit
The safety request is passed on to the servo drive on 2 channels via the inputs
#STO-A and #STO-B at the connection [X1A]. This safety request results in the
2-channel switch-off of the driver supply to the servo drive’s power output stage.
The safety relay unit can use the STA diagnostic output to monitor whether the
safe status has been reached for the safety sub-function STO.
SBC connection example
The safety sub-function SBC (safe brake control) is triggered by an input device
that makes the safety request.


































