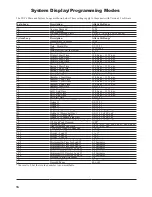
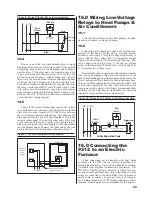
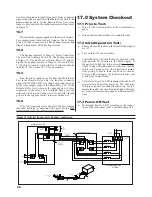
Appendix A — Glossary
12
The following terms are used throughout this manual
They are defi ned here to assist you in understanding their
meaning and use.
Average Demand:
The average rate of electric usage
during the demand averaging period. The average demand
is calculated by dividing the total number of kilowatt-hours
used by the number of hours in the averaging period. For
example, if 2 Kwh’s were used during an averaging period
of 15 minutes, the average demand would equal 2 divided
by .25 (15 minutes) or 8 KW.
Averaging Period:
An interval of 15, 30 or 60 minutes
over which the average demand is calculated. The 9312
should be set to the same averaging period as the utility’s
demand meter. (Same as Demand Interval)
Customer Charge:
A fl at charge on an energy bill
used to help the utility company recover fi xed costs
associated with serving a customer. It is independent of
the demand or consumption of the energy provided. Also
called monthly service charge or basic charge.
Declining Block Rate:
A method of charging for elec-
tric service used by electric utilities based on total energy
consumed (Kwh) and cost per Kwh. The cost per Kwh is
usually reduced in steps as total Kwh use increases.
Demand
: The rate of usage of electrical power,
expressed in KW (or kilowatts).
Demand Rate:
A method of charging for electric
service where the cost of electricity used is based on both
total energy consumed (Kwh) and peak demand (KW).
Demand Charge:
A charge that recovers some
of the utility’s capital and operating costs based on the
customer’s highest average use during the billing period. It
appears on an electric bill, along with the customer charge
and the energy charge.
Demand Interval:
Same as Averaging Period (see
above).
Demand Limit:
The set point, expressed in KW, is
the maximum energy is allowed to be consumed. As this
limit is approached, the Energy Sentry begins shutting off
pre-determined loads to control peak demand.
Demand Meter:
A utility meter which measures
both total energy consumed in Kwh and the highest peak
demand in KW.
Energy Charge:
This charge is for the energy con-
sumed during the billing period. It appears on the electric
bill, along with the customer charge and the demand
charge.
Energy Rate:
A method of charging for electric
service where the cost of electricity is based only on Kwh
consumption multiplied by a fi xed cost per Kwh. Cost per
Kwh remains the same regardless of the number of Kwh’s
used. Also called Flat Rate. Under this rate, demand is not
measured, recorded, or billed.
Instantaneous Demand:
The electricity in kilowatts
currently being drawn by the electrical service of a build-
ing at any instant in time.
Kilowatt (KW):
1,000 watts.
Kilowatt Hour (Kwh):
The basic measurement of
electric energy consumption as metered by the electric
utility. (If you were to turn on ten 100 watt lights for one
hour, you would have consumed one kilowatt hour of
electrical energy.)
Load:
The amount of electricity required by a particu-
lar energy consuming device or group of devices. Usually
expressed in watts or kilowatts.
Minimum Off-Time:
The minimum time that a
control point must be shut off before it can be restored by
the 9312. The Minimum Off-Time can be set from 0 to
20 minutes. Any control point having a heat pump or air
conditioner compressor or other motor load connected to
it should have a Minimum Off-Time of at least 4 minutes.
Resistive loads should not have Minimum Off-Times.
Minimum On-Time:
The minimum time that a control
point must be restored before it can be shed by the 9312.
The Minimum On-Time can be set from 0 to 20 minutes.
Any control point having a heat pump or air conditioner
compressor or other motor load connected to it should
have a Minimum On-Time of at least 5 minutes.
Peak Demand:
The highest usage in any demand
interval within the billing period.
Priority:
The relative importance of each controlled
load to all other controlled loads, as assigned in the 9312.
As the demand approaches the demand limit, the 9312
uses the priority of each load to determine which load(s)
to shed fi rst. A load with a priority of “1” is the highest
priority and is shed last and restored fi rst. A load with a
priority of “8” is the lowest priority and is shed fi rst and
restored last. Loads of equal priority will rotate being shed
and restored.
Time-Of-Use Demand Rate:
A method of charging
for electric service used by electric utilities which charges
a higher price for Kwh’s used in On-Peak periods, and a
lower price for Kwh’s used in the Off-Peak periods. The
demand peak is usually monitored and recorded only in the
On-Peak periods. The cost of electricity is based on both
total energy consumed (Kwh) and demand peak (KW).
Depending on the particular utility and rate, one or more
On-Peak periods, varying in length, may exist during a 24
hour period.
Watt:
A measure of electrical power or rate of doing
work. It is analogous to horsepower where one horsepower
is equivalent to approximately 746 watts.