3.5.1
JTAG on Module Connector
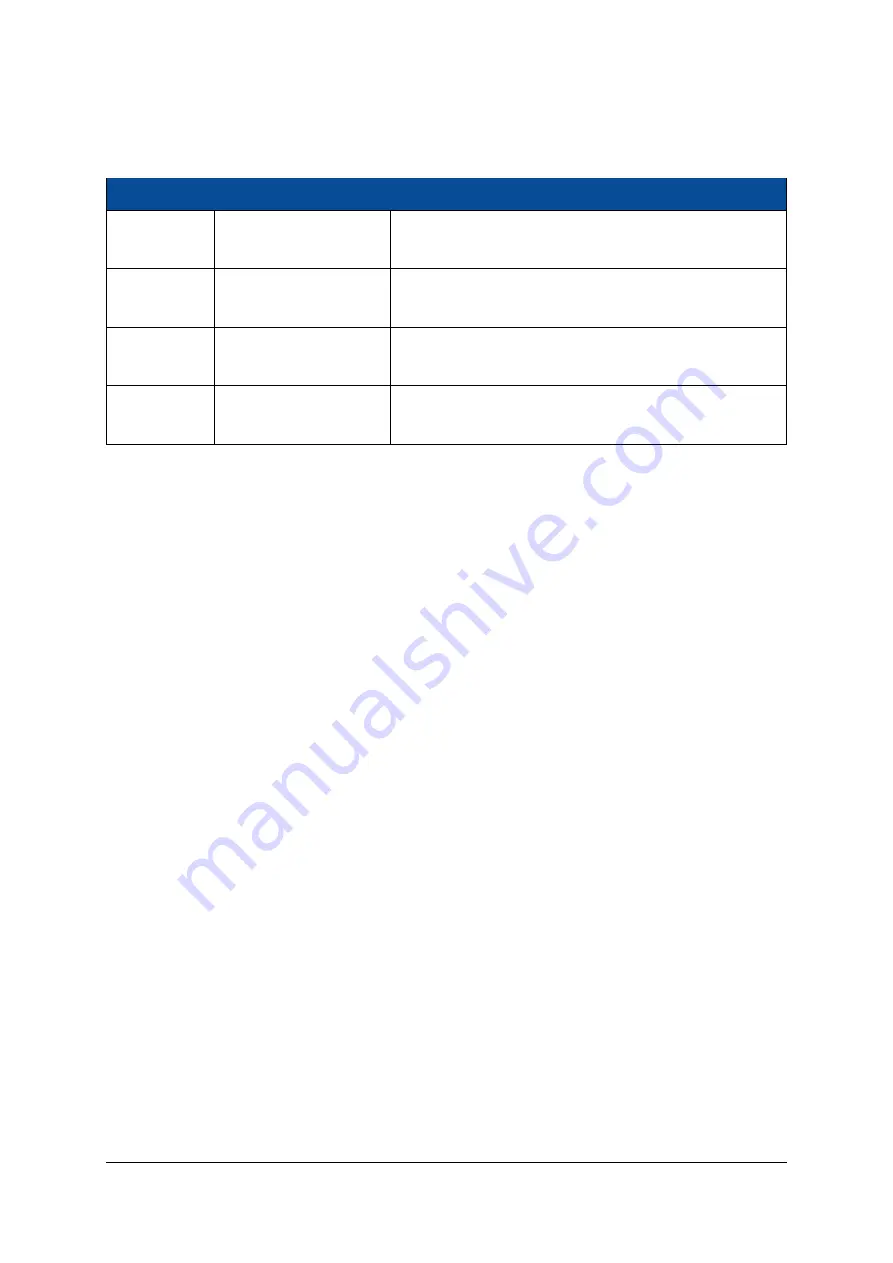
Signal Name
Module Connector Pin
Resistor
JTAG_TCK
A-123
10 k
Ω
pull-up to VCC_CFG_B14 (built-in in the level shifters
used by the JTAG circuit)
JTAG_TMS
A-119
10 k
Ω
pull-up to VCC_CFG_B14 (built-in in the level shifters
used by the JTAG circuit) and internal pull-up
JTAG_TDI
A-117
10 k
Ω
pull-up to VCC_CFG_B14 (built-in in the level shifters
used by the JTAG circuit) and internal pull-up
JTAG_TDO
A-121
10 k
Ω
pull-up to VCC_CFG_B14 (built-in in the level shifters
used by the JTAG circuit)
Table 30: JTAG Interface
3.5.2
External Connectivity
JTAG signals can be connected directly on the base board to a JTAG connector. No pull-up/pull-down re-
sistors are necessary. The VREF pin of the programmer must be connected to VCC_CFG_B14.
It is recommended to add 22
Ω
series termination resistors between the module and the JTAG header, close
to the source. Please refer to the Enclustra Module Pin Connection Guidelines for details on JTAG interface.
3.5.3
Xilinx JTAG Adapter
The KX2 FPGA module is equipped with a Xilinx JTAG adapter implemented using the FTDI device.
Port A of the FTDI device can be configured in synchronous FIFO mode or in Xilinx JTAG mode; please refer
to Section 3.10 for details.
3.6
Master Serial Configuration
In the master serial configuration mode, the FPGA reads the bitstream from the QSPI flash. The configuration
clock can be configured up to 22 MHz and quad-SPI booting is supported. Higher configuration clocks can
be achieved by using the advanced configuration settings of the Xilinx tools. For more information on the
configuration modes, please refer to the 7 Series FPGAs Configuration User Guide [17].
D-0000-430-002
34 / 48
Version 06, 25.07.2019














































