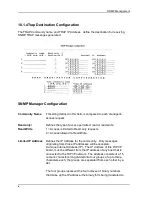
SNMP Management
Class C internet is expected to develop into many small networks with a few hosts on each.
It is assigned 15 network-bits and 3 host-bits.
Netid
Let the
Netid
be represented by: [
a b c
,
d e f
,
g h i
,
j k l
]
For Class A:
a b c
≠
0, unless the value of the
Slot IP Address
is [0.0.0.0]
0 <
a b c <
127
The following
Slot IP Addresses
are invalid: All [
abc
.255.255.255],
all [
abc
.0.0.0].
For Class B
128
≤
a b c
≤
191
The following
Slot IP Addresses
are invalid: [128.0.0.0], [191.255.0.0],
[
abc.def.
255.255], [
abc.def.
0.0.], [128.0.
ghi.jkl
], [191.255.
ghi.jkl
]
For Class C: 192
≤
a b c
≤
223
The following
Slot IP Addresses
are invalid: [192.0.0.0], [223.255.255.0],
all [192.0.0.
jkl
], all [223.255.255.
jkl
], [
abc.def.ghi.
0]
This screen includes several parameters that describe the TCP/IP Local Area Network. Be
sure to define
Slot IP Address
and
Subnet Mask
since they do not have default values. As
you define each parameter, its value will accumulate in the Controller's memory; the
Controller will save the values only after you've defined all the parameters. Special
messages will indicate the undefined fields.
Configuring for SNMP agent functionality
1. Access the SNMP Configuration menu by entering the SNMP Configuration option from
the 3494 Setup menu.
2. Enable Controller SNMP agent monitoring, and define the essential parameters.
3. Define the number of IP gateways (only if the SNMP manager must be accessed via a
router).
4. For each of the number of gateways assigned, define the essential parameters
Gateways IP Address, and Gateways Net ID.
5. Define the relevant SNMP manager parameters (optional).
6. If you want TRAPs sent to the manager under specific conditions, enable either one or
both groups of TRAPs.
2
Содержание 3000 Series
Страница 1: ...Series 3000 STK3494 3494 User s Manual ...
Страница 2: ......