Chapter 6 Fault diagnosis and solutions VFD500 high performance vector control frequency inverter user manual
Chapter 6 Fault Diagnosis and Solution
6.1 Failure and diagnosis
The VFD500 inverter has perfect protection. If a fault occurs, the inverter will act according to the fault
attribute. For more serious faults, the inverter will directly block the output; for general faults, it can be
configured to stop or continue to operate according to the scheduled stop mode. After the inverter fails,
the fault relay contacts act and the fault code is displayed on the display panel. Before seeking service,
users can perform self-checking according to the tips in this section, analyze the cause of the fault, and
find a solution.
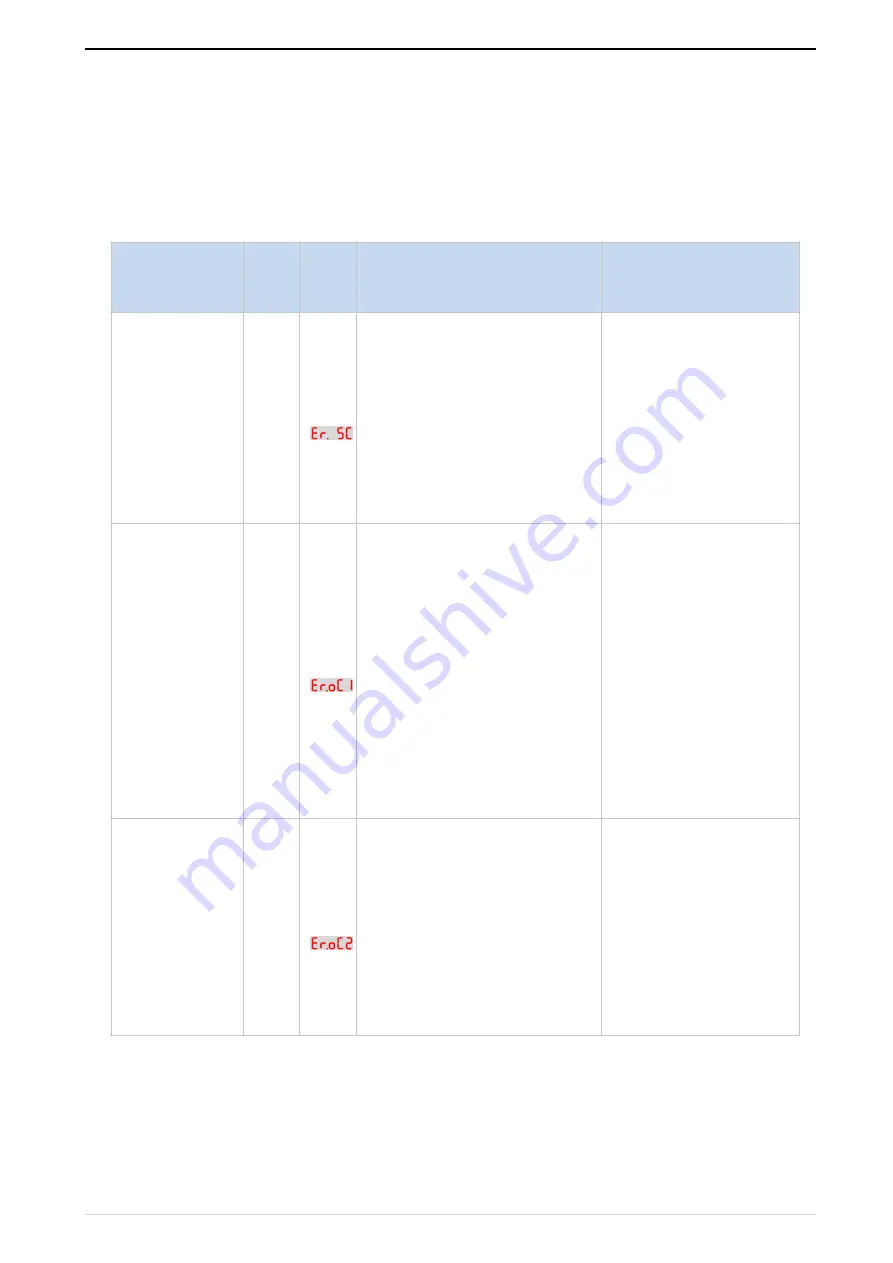
Fault Name
Faul
t
cod
e
Disp
lay
Possible Causes
Solutions
Inverter unit
protection
1
1: Motor insulation aging
2: The cable is damaged and
contact, short circuit
3:The distance between motor
and inverter are too long.
4: Output transistor breakdown
5: The internal wiring of the
inverter is loose, or the hardware
is bad.
6:Brake transistor short circuit
1. Confirm the insulation
resistance of the motor. If
it is turned on, replace the
motor.
2. Check the power cable
of the motor
3. Install reactor or output
filter
4, seeking technical
support
5, seeking technical
support
Over current
during
acceleration
2
1: The output circuit is grounded
or
short circuited.
2: Motor auto-tuning is not
performed.
3: The acceleration time is too
short.
4: Manual torque boost or V/F
curve is
not appropriate.
5: The voltage is too low.
6: The startup operation is
performed
on the rotating motor.
7: A sudden load is added during
acceleration.
1: Eliminate external
faults.
2: Perform the motor
auto-
Tuning in cold state
3: Increase the
acceleration
time.
4: Adjust the manual
torque
boost or V/F curve.
5: Adjust the voltage to
normal
range.
6: Select rotational speed
tracking restart or start
the
Over current
during
deceleration
3
1: The output circuit is grounded
or
short circuited.
2: Motor auto-tuning is not
performed.
3: The deceleration time is too
short.
4: The voltage is too low.
5: A sudden load is added during
deceleration.
6: The braking unit and braking
resistor are not installed
1: Eliminate external
faults.
2: Perform the motor
auto-tuning.
3: Increase the
deceleration time.
4: Adjust the voltage to
normal
range.
5: Remove the added
load.
6: Install the braking unit
Er.O
C1
Er.
SC
Er.O
C2
111