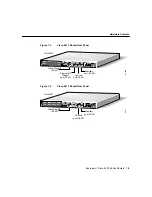
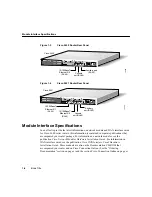
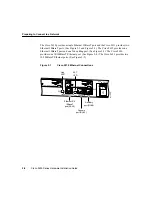
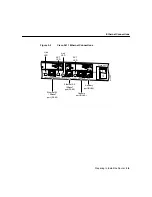
Preparing to Install the Router 2-7
Preparing to Connect to a Network
Preparing to Connect to a Network
When setting up your router, consider distance limitations and potential electromagnetic
interference (EMI) as defined by the applicable local and international regulations.
Network connection considerations are provided for several types of network interfaces and
are discussed in the following sections:
•
Ethernet Connections on page 2-7
•
Token Ring Connections on page 2-12
•
Serial Connections on page 2-14
•
ISDN BRI Connections on page 2-22
•
56K/Switched-56-kbps DSU/CSU Connections on page 2-23
Ethernet Connections
The IEEE has established Ethernet as standard IEEE 802.3. The most common Ethernet
implementations are as follows:
•
100BaseT—2-pair Category 5 or unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) straight-through RJ-45
cable.
•
10Base2—Ethernet on thin coaxial cable, also known as thin Ethernet. The maximum
segment distance is 607 feet (186 meters).
•
10Base5—Ethernet on thick coaxial cable, also known as thick Ethernet. The maximum
segment distance is 1,640 feet (500 meters).
•
10BaseT—Ethernet on UTP cable. The maximum segment distance is 328 feet (100
meters). UTP cables look like the wiring used for ordinary telephones; however, UTP
cables meet certain electrical standards that telephone cables do not meet.
The Ethernet interfaces available for the Cisco 2610, Cisco 2611, and Cisco 2612 routers
operate at speeds up to 10 Mbps. The Ethernet interfaces available for the Cisco 2620 and
Cisco 2621 routers operate at speeds up to 100 Mbps.
Warning
The Ethernet 10BaseT, Token Ring, console, and auxiliary ports contain safety
extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits. Avoid connecting SELV circuits to TNV circuits.