Appendix B: Troubleshooting
Check the following first:
Make sure that the power of the gateway is on and the Ethernet cables are connected firmly to
the RJ-45 jacks of the gateway.
Make sure that the LED ALV of the gateway is blinking to indicate the gateway is working.
Make sure the types of the Ethernet cables are correct. Recall that there are two types—
normal
and
crossover
.
Make sure that the DSL, cable, V.90, or ISDN modem connected with the gateway is powered
on.
B-1: TCP/IP Settings Problems
ADSL/Cable/
V.90/ISDN
Modem
Default Gateway
of AG
Ethernet/
RS232
WLAN Access
Gateway (AG)
Stage A
State B
Stage C
Correspondent
Host
Stage D
Wireless Client
Computer
DNS Server
of AG
Phone/
CATV
Network
Internet
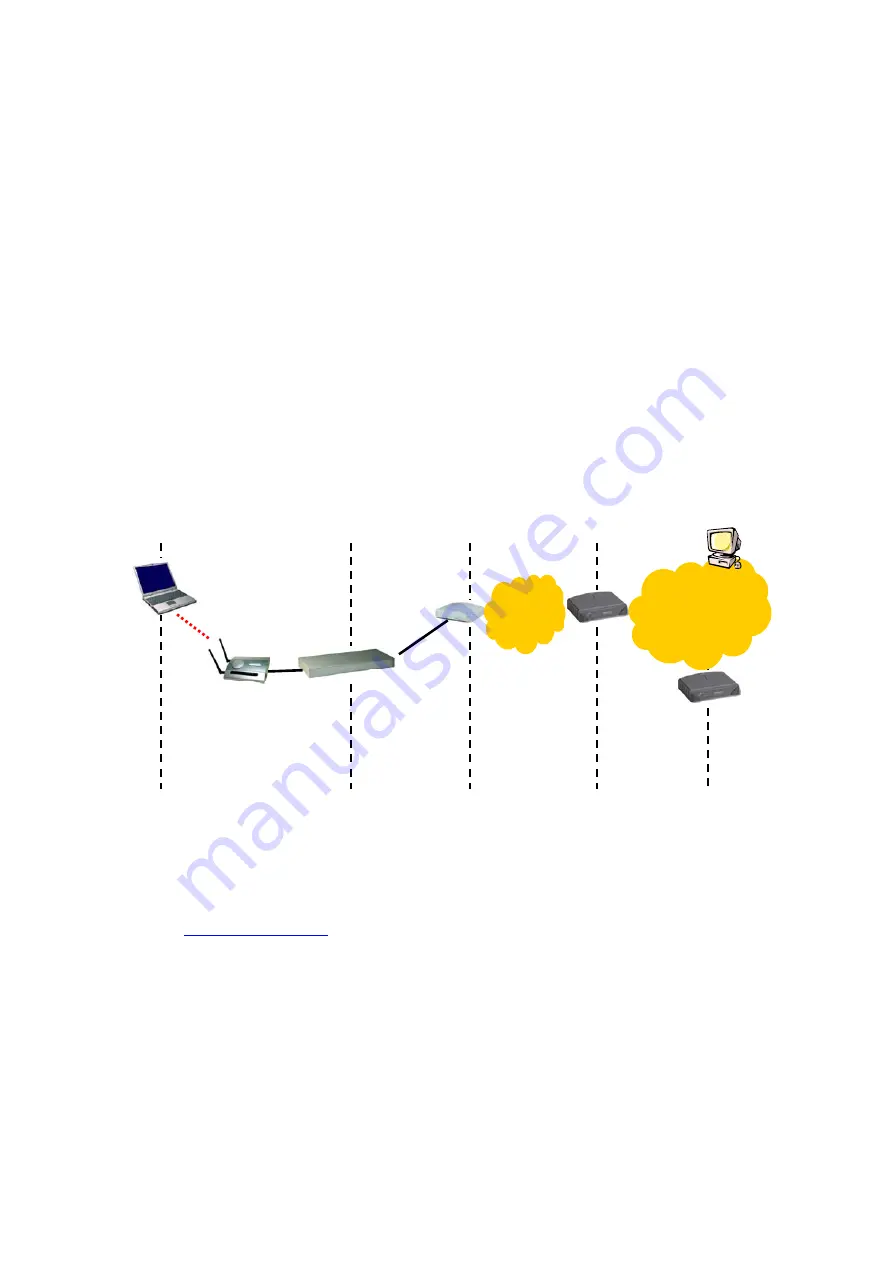
Fig. 109. Communication stages for a client to reach its correspondent host.
For a client computer to communicate with a correspondent host on the Internet by the host’s domain
name (e.g.
), it first sends a DNS request to a DNS server on the Internet. The
DNS request travels first to the WLAN hotspot access gateway, then the WLAN hotspot access gate-
way relays this request to the default gateway of the WLAN hotspot access gateway through a modem.
Finally, this request is forwarded by the default gateway to the DNS server on the Internet. The DNS
reply issued by the DNS server is transmitted back to the client computer following a reverse path.
When the client computer receives the DNS reply, it knows the IP address of the correspondent host
and sends further packets to this IP address.
As illustrated in Fig. 109, the communication path could be broken at some of the stages. The
OS-provided network diagnostic tool,
ping.exe
, can be employed to find out TCP/IP-related commu-
nication problems.
75
Содержание IWE1200A-G
Страница 1: ...USER S MANUAL...
Страница 14: ...7...
Страница 72: ...Fig 95 Advertisement links settings Fig 96 Advertisement links in action 65...






































