SERIES IP236 INDUSTRIAL I/O PACK FIFO BUFFERED 16 BIT ANALOG OUTPUT MODULE
___________________________________________________________________________________________
- 5 -
The board may be configured differently, depending on the
application. Jumper settings are discussed in the following
sections. The jumper locations are shown in Drawing 4501-735.
Default Hardware Jumper Configuration
The board is shipped from the factory, configured as follows:
•
Each analog output range is configured for a bipolar output
with a 20 volt span (i.e. a DAC output range of -10 to +10
Volts).
•
The default programmable software control register bits at
power-up are described in section 3. The control registers
must be programmed to the desired mode before starting
DAC analog output conversions.
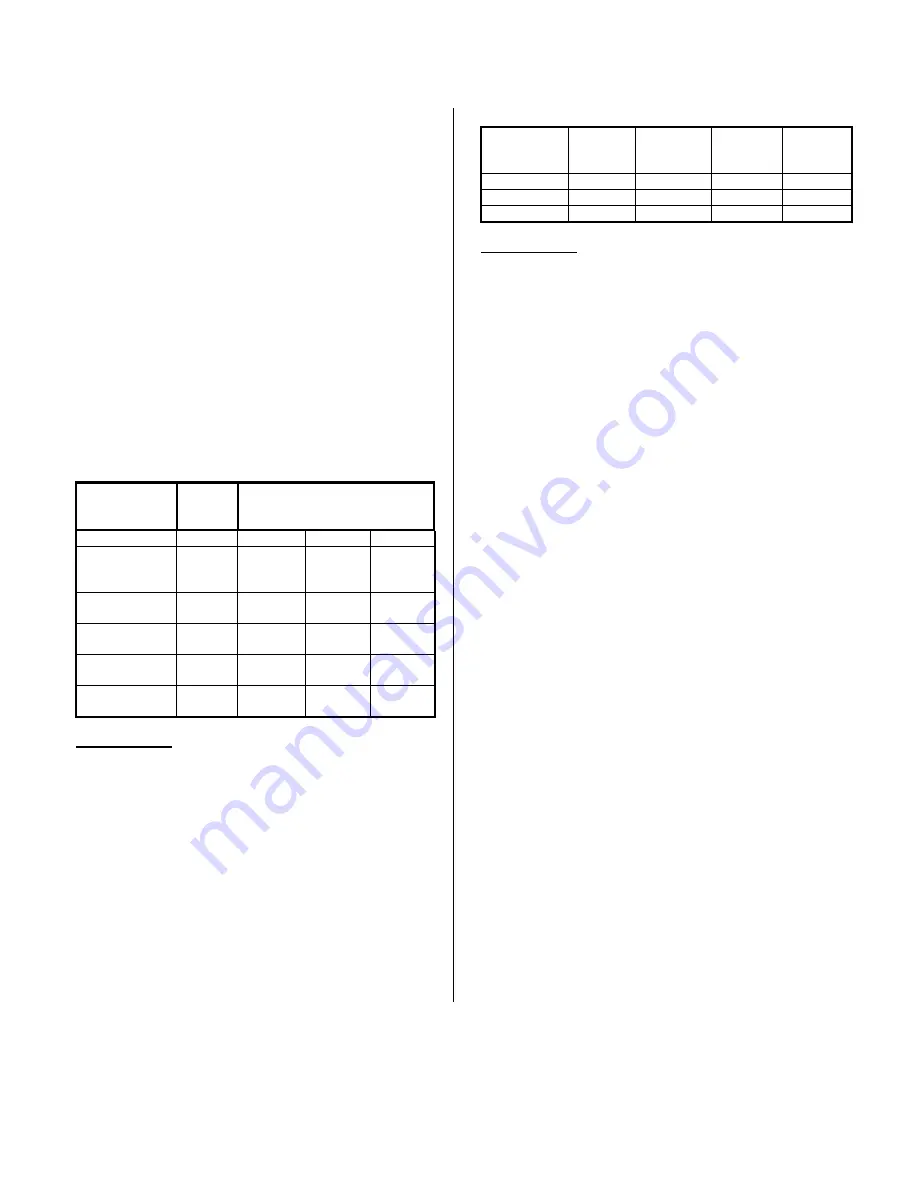
Analog Output Ranges and Corresponding Digital Codes
The IP236 is designed to accept positive-true binary two’s
complement (BTC) input codes which are compatible with bipolar
analog output operation. Table 2.1 indicates the relationship
between the data format and the ideal analog output voltage for
each of the analog output ranges. Selection of an analog output
range is implemented via the jumper setting given in Table 2.2.
Table 2.1: Full-Scale Ranges and Ideal Analog Output
DESCRIPTION
Digital
Input
Code
ANALOG OUTPUT
Output Range
±
10V
0 to 10V
±
5V
LSB (Least
Significant Bit)
Weight
305
µ
V
153
µ
V
153
µ
V
Plus Full Scale
Minus One LSB
7FFF
H
9.999695
Volts
9.999847
Volts
4.999847
Volts
Midscale
0000
H
0V
1
5V
1
0V
1
One LSB Below
Midscale
FFFF
H
-305
µ
V
4.999847
Volts
-153
µ
V
Minus Full
Scale
8000
H
-10V
0V
-5V
Notes (Table2.1):
1. Upon power-up or software reset the bipolar ranges will
output 0 volts while the unipolar range will output 5 volts.
Analog Output Range Hardware Jumper Configuration
The output range of the DACs are individually programmed
via hardware jumpers J1 to J8. Jumpers J1 to J8 are used to
control channels 0 to 7, respectively. The jumpers control the
output voltage span and the selection of unipolar or bipolar output
ranges. J1 to J8 pins 1 and 2 control the selection of unipolar or
bipolar output ranges. J1 to J8 pins 3 and 4 control the selection
of output voltage span. The configuration of the jumpers for the
different ranges is shown in Table 2.2. “ON” means that the pins
are shorted together with a shorting clip. “OFF” means that the
clip has been removed. The individual jumper locations are
shown in Drawing 4501-735.
Table 2.2: Analog Output Range Selections/Jumper Settings
Desired
ADC Output
Range (VDC)
Output
Span
(Volts)
Required
Output
Type
J1 to J8
Pins (1&2)
J1 to J8
Pins (3&4)
-5 to +5
10
Bipolar
ON
ON
-10 to +10
1
20
Bipolar
ON
OFF
0 to +10
10
Unipolar
OFF
ON
Notes (Table2.2):
1. The board is shipped with the default jumper setting for the
±
10 volt DAC output range.
Software Configuration
Software configurable control registers are provided for
control of external trigger mode, conversion mode, timer control,
and interrupt mode selection. No hardware jumpers are required
for control of these functions. These control registers must also
be configured as desired before starting DAC analog output
conversions. Refer to section 3 for programming details.
CONNECTORS
Connectors of the IP236 module consist of one IP module
field I/O connector, and one IP module logic connector. These
interface connectors are discussed in the following sections.
IP Field I/O Connector (P2)
P2 provides the field I/O interface connections for mating IP
modules to the carrier board. P2 is a 50-pin female receptacle
header (AMP 173279-3 or equivalent) which mates to the male
connector of the carrier board (AMP 173280-3 or equivalent).
This provides excellent connection integrity and utilizes gold-
plating in the mating area. Threaded metric M2 screws and
spacers are supplied with the module to provide additional
stability for harsh environments (see Mechanical Assembly
Drawing 4501-434). The field and logic side connectors are
keyed to avoid incorrect assembly.
P2 pin assignments are unique to each IP model (see Table
2.3) and normally correspond to the pin numbers of the field I/O
interface connector on the carrier board (you should verify this for
your carrier board). When reading Table 2.3 note that channel
designations are abbreviated to save space. For example,
channel 0 is abbreviated as “+CH00” & “-CH00” for the + & -
connections, respectively. Further, note that the output signals
all have the same ground reference (“-CH00” and the minus leads
of all other channels are connected to analog common on the
module).






































