11
25
A1
First channel MODBUS
communication
26
B1
28
A2
Second channel MODBUS
communication
29
B2
32
T1
(
PTC input A
)
Temperature protection (thermistor
input)
33
T2
(
PTC input B
)
41
IO*
Leakage current measurement
42
COM3(common terminal of current
、
leakage
current input )
Three phase current input
43
Ia Phase current input
44
Ib Phase current input
45
Ic Phase current input
6
6
6
6 Protection
Protection
Protection
Protection function
function
function
function description
description
description
description
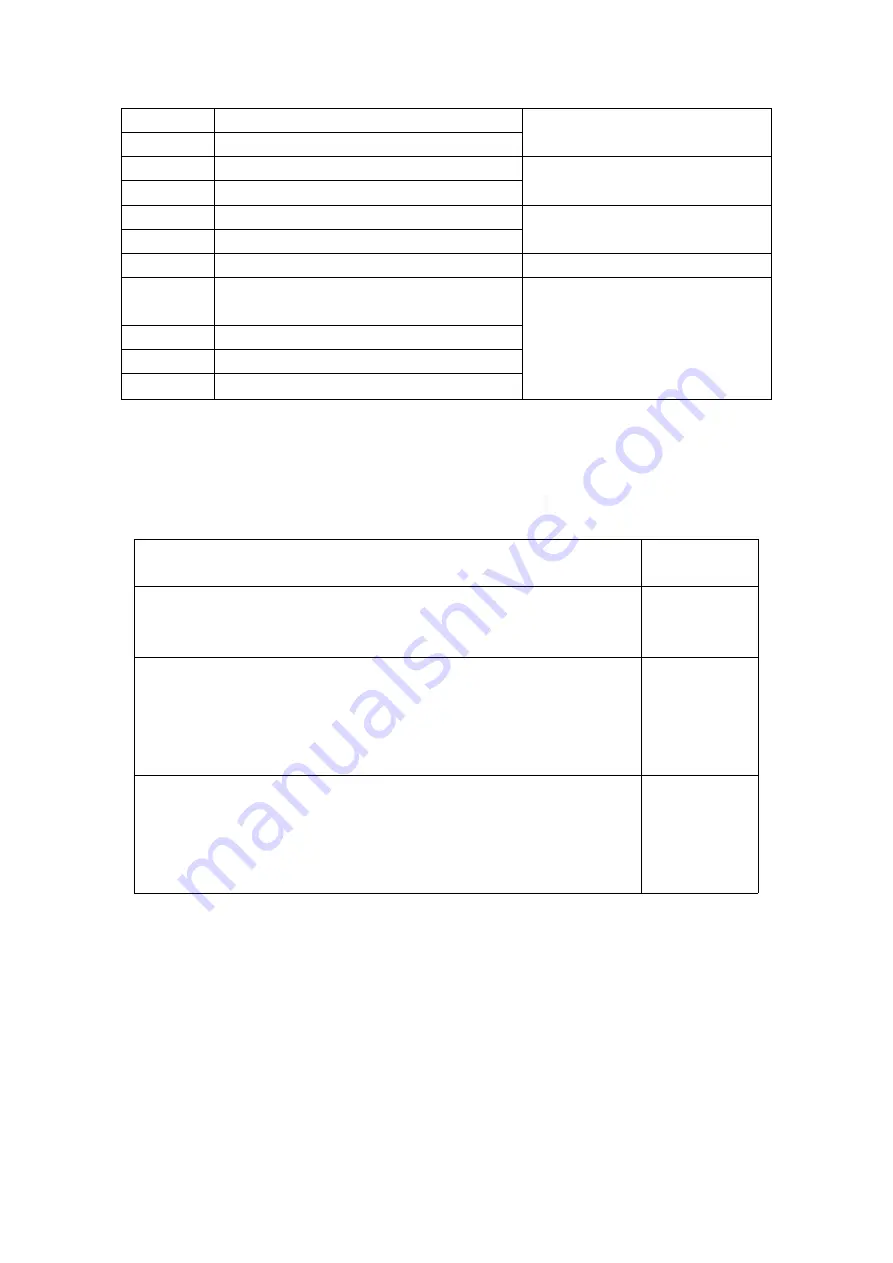
The default action stages of each protection are shown in Table 8
:
Table 8
Protection type
Default active
period
Overvoltage, undervoltage, voltage imbalance, phase sequence, external
fault, overflow protection, starting times, fault times, running time,
PTC/NTC temperature protection
Reverse time overload, locked rotor, phase break, leakage, grounding,
starting timeout, short circuit, overflow protection,
Overvoltage, undervoltage, voltage imbalance, phase sequence, external
fault, number of starts, number of faults, running time, PTC/NTC
temperature protection, fixed time overload
When
starting
Reverse time-limit overload, blocking, phase break, current imbalance,
leakage, grounding, constant time-limit overload, underload, short circuit,
overflow protection, overvoltage, undervoltage, voltage unbalance, phase
sequence, underpower, overpower, external fault, PTC/NTC temperature
protection, number of starts, number of faults, running time
In operation
6.1 Inverse time overload protection
When the motor runs for a long time in excess of its rated current under excessive load, it
will overheat the motor, reduce insulation and burn it out. The protector calculates the heat
capacity of the motor according to its heating characteristics and simulates its heating
characteristics to protect the motor.
The starting condition of reverse time-limit overload protection is that the maximum
three-phase current reaches the set overload starting value, and the default overload starting value
is 1.2 times the motor's rated current.
The current-time comparison table of overload protection is shown in Table 9, and the
overload characteristic curve (K curve) is shown in Figure 10:















































