41-2
ing application
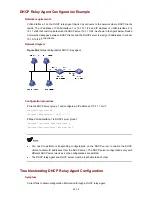
Figure 41-1
Typical network diagram for DHCP snoop
DHCP Client DHCP Client
Switch A
(DHCP Snooping)
Internet
Eth1/0/2
Eth1/0/1
Switch B
(DHCP Relay)
DHCP Client
DHCP Client
DHCP Server
z
DHCP-REQUEST packet
Introduction to DHCP-Snooping Option 82
Introduction to Option 82
For details about Option 82, refer to
Option 82 Sup
DHCP snooping listens the following two types of packets to retrieve the IP addresses the DHCP clients
obtain from DHCP servers and the MAC addresses of the DHCP clients:
z
DHCP-ACK packet
port on DHCP Relay Agent
.
Padding content
of
There is no specifi
hat should
.
By default, the sub-options of Option 8
CP
s
re padd
z
sub-option 1
ption)
al port
number by 1) and VLAN ID of the port
quest.
z
sub-option 2
ption):
device that re
y default, when S4500 Series Ethernet Switches serve as DHCP snooping devices, Option 82 adopts
and frame format
cation for w
Option 82
be padded in Option 82. Manufacturers can pad it as required
2 for S4500 Series Ethernet Switches (enabled with DH
nooping) a
ed as follows:
(circuit ID sub-o
: Padded with the port index (smaller than the physic
that received the client’s re
(remote ID sub-o
ceived the client’s requ
Padded with the bridge MAC address of the DHCP snooping
est.
B
the extended format. Refer to
Figure 41-2
and
Figure 41-3
for the extended format of the sub-options
(with the default padding contents). That is, the circuit ID or remote ID sub-option defines the type and
length of a circuit ID or remote ID.
The remote ID type field and circuit ID type field are determined by the option storage format. They are
both
rmat and to
1
in
Figure 41-2
Extended format of the circ
set to
0
in the case of HEX fo
the case of ASCII format.
uit ID sub-option