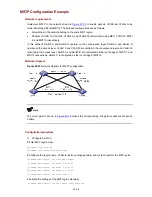
23-2
: Cost from the local router to the destination.
time: Time elapsed since the routing entry was last updated. The time is reset to 0 every time
RIP timers
Gar
z
z
n it is deleted from the routing table. During the Garbage-Collect timer
e route with the routing metric set to 16. If no update is announced for that
Routing loops preventi
is a dist
z
achable. When a routing loop occurs,
the metric value of the route will increment to 16.
oes not send the routing information learned from a neighbor back to the
RIP S
t
The
tion is as follows:
z
t, it updates its local routing table and sends a
z
intain their own routing tables and select optimal routes, and then
advertise update information to their respective neighbors so as to make the updated routes known
he aging mechanism to handle the timeout routes to ensure
real-time and valid routes.
RIP Configuration Task List
C
ng
z
Interface: Outbound interface on this router, through which IP packets should be forwarded to
reach the destination.
z
Metric
z
Route
the routing entry is updated.
As defined in RFC 1058, RIP is controlled by three timers: Period update, Timeout, and
bage-collection.
z
Period update timer: The period update timer defines the interval between routing updates.
Timeout timer: The timeout timer defines the route aging time. If no update for a route is received
after the aging time elapses, the metric of the route is set to 16 in the routing table.
Garbage-collection timer: The garbage-collect timer defines the interval from when the metric of a
route becomes 16 to whe
length, RIP advertises th
route after the Garbage-Collect timer expires, the route will be deleted from the routing table.
on
RIP
ance-vector (D-V) based routing protocol. Since a RIP router advertises its own routing
table to neighbors, routing loops may occur.
RIP uses the following mechanisms to prevent routing loops.
Counting to infinity. The metric value of 16 is defined as unre
z
Split horizon. A router d
neighbor to prevent routing loops and save the bandwidth.
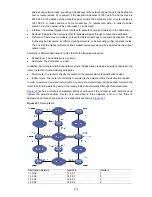
tar up and Operation
whole process of RIP startup and opera
z
Once RIP is enabled on a router, the router broadcasts or multicasts a request packet to its
neighbors. Upon receiving the packet, each neighbor running RIP answers a response packet
containing its routing table information.
When this router receives a response packe
triggered update packet to the neighbors. Upon receiving the triggered update packet, the neighbor
sends the packet to all its neighbors. After a series of update triggering processes, each router can
get and keep the updated routing information.
By default, RIP sends its routing table to its neighbors every 30 seconds. Upon receiving the
packets, the neighbors ma
globally. Furthermore, RIP uses t
omplete the followi
tasks to configure RIP: