Performance specifications
000000-1520-928_GA_EN_021013
14
The wavefront map is uniformly colored for an eye with normal vision
(emmetropic). If the eye exhibits refractive errors, these will be shown color-
coded in the wavefront map: Short-sightedness (myopia) and farsightedness
(hyperopia) manifest themselves in wavefront maps that have spherical caps
curved to the inside or outside. Astigmatism appears in the form of elliptical
contours (areas of the same color) in the wavefront map with the elliptical
axis along the astigmatism axis. Other abnormalities (higher order
aberrations) result in characteristic irregular structures in the wavefront map.
A wavefront measurement is only a snapshot of the optical state of the
patient's eye. It is not a fixed parameter for the eye and depends on the
accommodation state.
Topography measurement
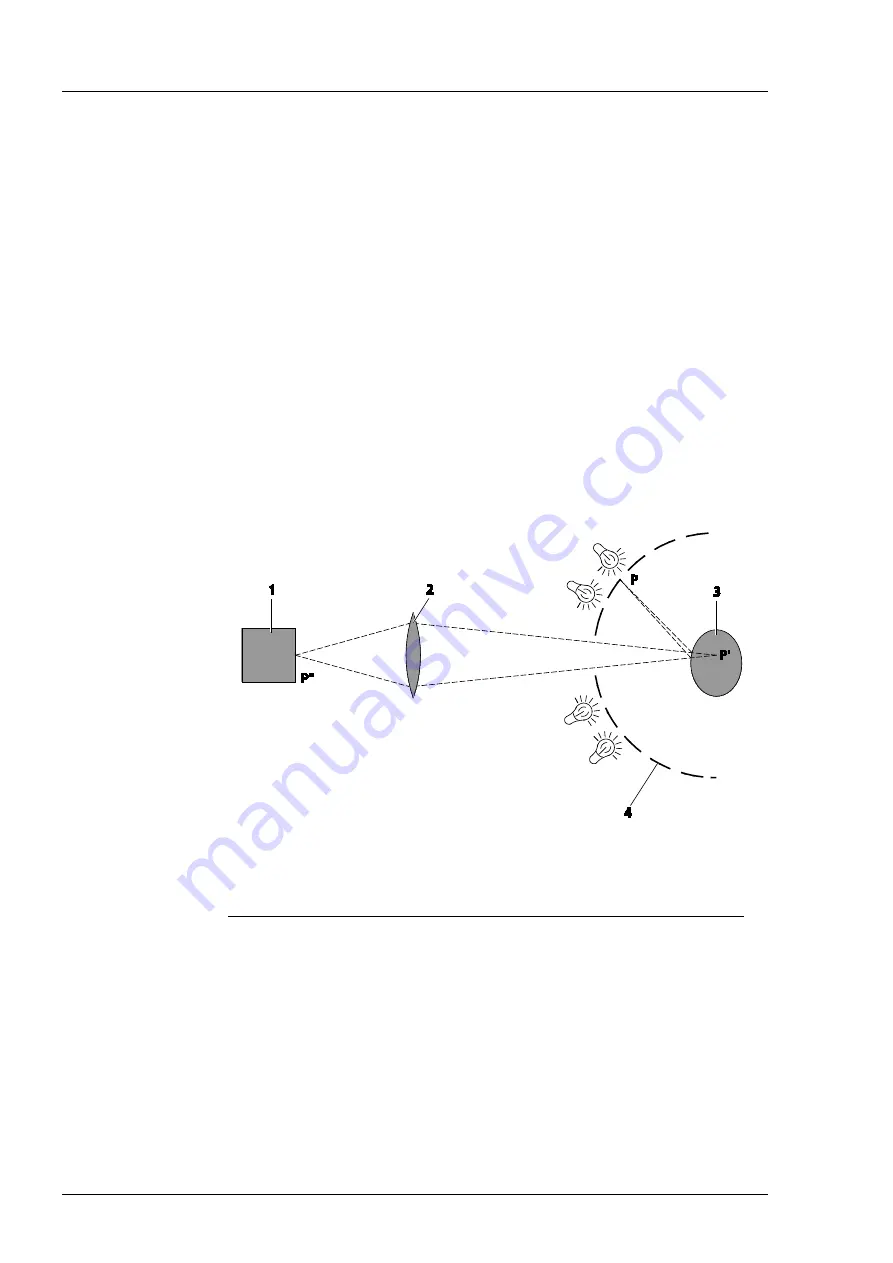
The topography of the cornea is measured with a Placido disc. The diagram
(Fig. 4) demonstrates the optical imaging in simplified form.
1
Camera
2
Lens
3
Eye
4
Placido disc with illuminated rings
Fig. 4
Imaging beam path of a topography measuring device with a Placido disc.
A light pencil originating at point P is reflected by the mirroring, convex surface of
the cornea. The virtual point P' is reproduced via a lens to the camera P''.






























