FORM 160.55-O1 (920)
149
YORK INTERNATIONAL
LD00475
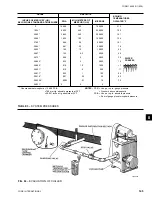
FIG. 65 –
DIAGRAM, MEGGING MOTOR WINDINGS
GENERAL
Maintenance of condenser and cooler shells is im-
portant to provide trouble free operation of the chiller.
The water side of the tubes in the shell must be kept
clean and free from scale. Proper maintenance such as
tube cleaning, and testing for leaks, is covered on the
following pages.
CHEMICAL WATER TREATMENT
Since the mineral content of the water circulated through
coolers and condensers varies with almost every source
of supply, it is possible that the water being used may
corrode the tubes or deposit heat resistant scale in them.
Reliable water treatment companies are available in most
larger cities to supply a water treating process which will
greatly reduce the corrosive and scale forming properties
of almost any type of water.
As a preventive measure against scale and corrosion
and to prolong the life of cooler and condenser tubes, a
chemical analysis of the water should be made preferably
before the system is installed. A reliable water treatment
company can be consulted to determine whether water
treatment is necessary, and if so, to furnish the proper
treatment for the particular water condition.
CLEANING COOLER AND CONDENSER TUBES
Cooler
It is difficult to determine by any particular test whether
possible lack of performance of the water cooler is due
to fouled tubes alone or due to a combination of troubles.
Trouble which may be due to fouled tubes is indicated
when, over a period of time, the cooling capacity de-
creases and the split (temperature difference between
water leaving the cooler and the refrigerant temperature
in the cooler) increases. A gradual drop-off in cooling
capacity can also be caused by a gradual leak of refrig-
erant from the system or by a combination of foul ed
tubes and shortage of refrigerant charge. An excessive
quantity of oil in the cooler can also contribute to erratic
performance.
Condenser
In a condenser, trouble due to fouled tubes is usually
indicated by a steady rise in head pressure, over a period
of time, accompanied by a steady rise in condensing
temperature, and noisy operation. These symptoms may
also be due to foul gas buildup. Purging will remove the
foul gas revealing the effect of fouling.
TUBE FOULING
Fouling of the tubes can be due to deposits of two types
as follows:
1. Rust or sludge, which finds its way into the tubes
and accumulates there. This material usually does
not build up on the inner tube surfaces as scale, but
does interfere with heat transfer. Rust or sludge can
generally be removed from the tubes by a thorough
brushing process.
2. Scale, due to mineral deposits. These deposits, even
though very thin and scarcely detectable upon phys-
ical inspection, are highly resistant to heat transfer.
They can be removed most effectively by circulating
an acid solution through the tubes.
CONDENSERS AND COOLERS
8