2. When required by local codes, a manual shut-off valve may
have to be installed outside of the unit.
3. Use wrought iron or steel pipe for all gas lines. Pipe dope
should be applied sparingly to male threads only.
WARNING: Natural gas may contain some propane. Propane,
being an excellent solvent, will quickly dissolve white
lead or most standard commercial compounds.
Therefore, a special pipe compound must be applied
when wrought iron or steel pipe is used. Shellac base
compounds such as Gaskolac or Stalastic, and com-
pounds such as Rectorseal #5, Cyde’s or John
Crane may be used.
4. All piping should be cleaned of dirt and scale by hammering
on the outside of the pipe and blowing out the loose dirt and
scale. Before initial start-up, be sure that all of the gas lines
external to the unit have been purged of air.
5. The gas supply should be a separate line and installed in
accordance with all safety codes as prescribed under “Limi-
tations”. After the gas connections have been completed,
open the main shut-off valve admitting
normal gas pressure
to the mains. Check all joints for leaks with soap solution or
other material suitable for the purpose. NEVER USE A
FLAME.
6. The furnace and its individual manual shut-off valve must be
disconnected from the gas supply piping system during any
pressure testing of that system at test pressures in excess of
1/2 psig (3.48kPa).
The furnace must be isolated from the gas supply piping
system by closing the individual manual shuff-off valve during
any pressure testing of the gas supply system at test
pressures equal to or less than 1/2 psig (3.48kPa).
7. A 1/8 inch NPT plugged tapping, accessible for test gage
connection, must be installed immediately upstream of the
gas supply connection to the furnace.
COMBUSTION DISCHARGE
The products of combustion are discharged horizontally through
a screened (hooded) opening on the upper gas heat access
panel.
GAS PIPING
Proper sizing of gas piping depends on the cubic feet per hour
of gas flow required, specific gravity of the gas and the length
of run. “National Fuel Gas Code” Z223.1 should be followed in
all cases unless superseded by local codes or gas company
requirements. Refer to Table 3.
The heating value of the gas may differ with locality. The value
should be checked with the local gas utility.
NOTE: There may be a local gas utility requirement specifying
a minimum diameter for gas piping. All units require a
1/2 or 3/4 inch pipe connection at the gas valve.
GAS CONNECTION
The gas supply line can be routed through the knockouts located
on the front of the unit or through the opening provided in the
unit’s base. Refer to Figure 10 to locate these access openings.
Typical supply piping arrangements are shown in Figures 5 and
6. All pipe nipples, fittings and the gas cock are field-supplied.
A gas piping kit (1GP0402) is available for bottom supply with
external shutoff.
Two grommets are shipped in the blower compartment (in parts
bag taped to the blower housing) of every unit with gas heat and
should be used in the knockouts when the gas piping penetrates
the front of the unit.
After the gas supply piping has been installed, the bottom
opening should be sealed to prevent water from leaking into the
building.
Gas piping recommendations:
1. A drip leg and a ground joint union must be installed in the
gas piping.
Input
Capacity,
(Mbh)
Output
Capacity,
(Mbh)
Available on
Models
Gas Rate
1
(Ft.
3
/Hr.)
Temp. Rise
°
F
At Full Input
2
Min.
Max.
163
130
7
1
⁄
2
Ton
152
30
60
204
163
7
1
⁄
2
- 12-1/2 Ton
190
30
60
245
198
10 & 12-1/2 Ton
228
30
60
NOTE: Gas Heaters are shipped available for natural gas, but can be converted to L.P. with
Kit Model No. 1NP0421 (USA). All furnaces meet the latest California seasonal
efficiency requirements.
1
Based on 1075 Btu/Ft
3
.
2
The air flow must be adjusted to obtain a temperature rise within the range shown.
TABLE 2 - GAS HEAT APPLICATION DATA
Length in Feet
Nominal Iron Pipe Size
1/2 in.
3/4 in.
1 in.
1-1/4 in.
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
132
92
73
63
56
50
46
43
40
38
278
190
152
130
115
105
96
90
84
79
520
350
285
245
215
195
180
170
160
150
1,050
730
590
500
440
400
370
350
320
305
Maximum capacity of pipe in cubic feet of gas per hour. (Based upon a pressure drop of 0.3
inch water column and 0.6 specific gravity gas).
TABLE 3 - PIPE SIZING
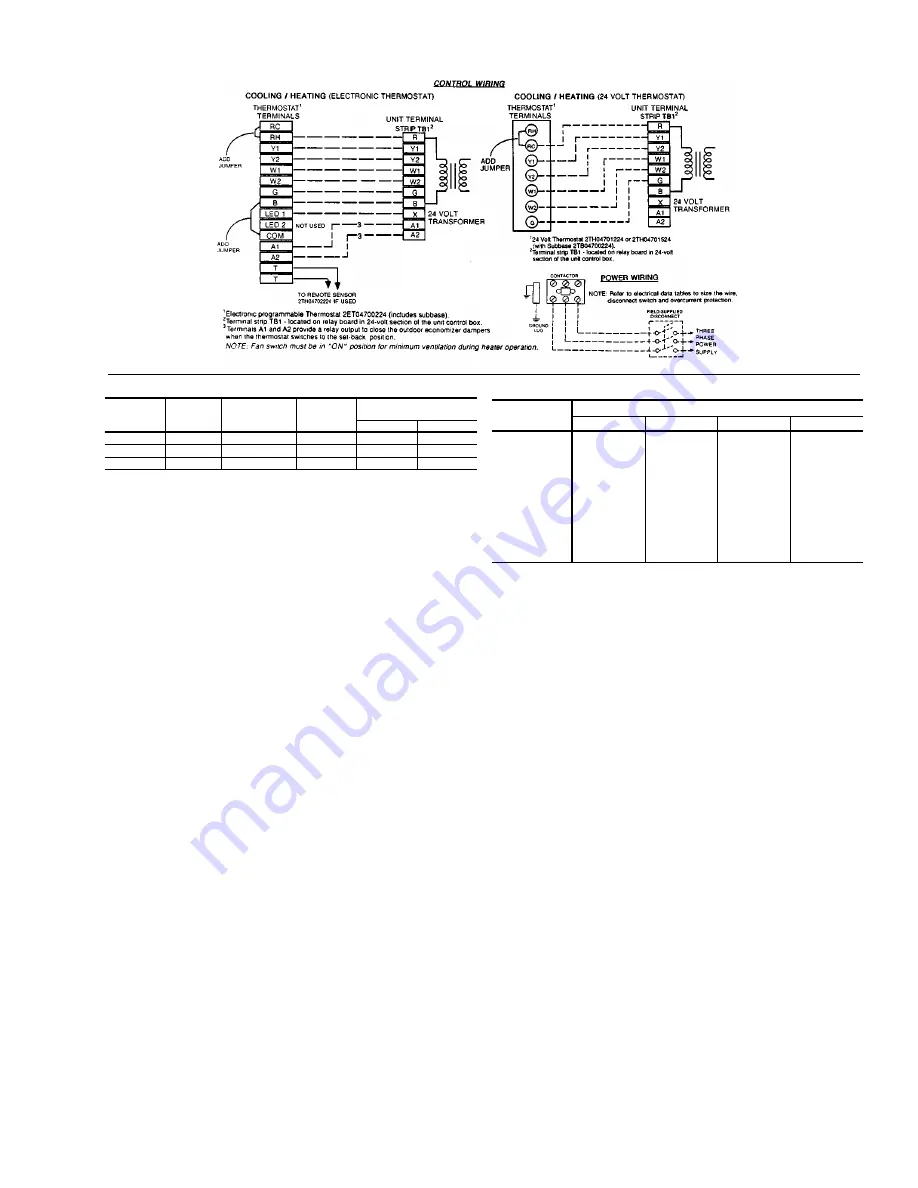
FIG. 4 - TYPICAL FIELD WIRING
530.22-N4Y
Unitary Products Group
5




















