Introduction – What to read?
Waldorf Q User’s Manual
14
If you are a synthesizer hotshot
Do you own
a whole bunch
of various synthesizers of all flavours, analog, digital, sample playback,
and know how to
create
and
modify
sounds, multis and other patch types on them? Do you already
own any Waldorf synthesizers so that you are familiar with their structure and terminology. Then
make sure to read at least the following chapters. They describe the extraordinary features and
functions of the Q.
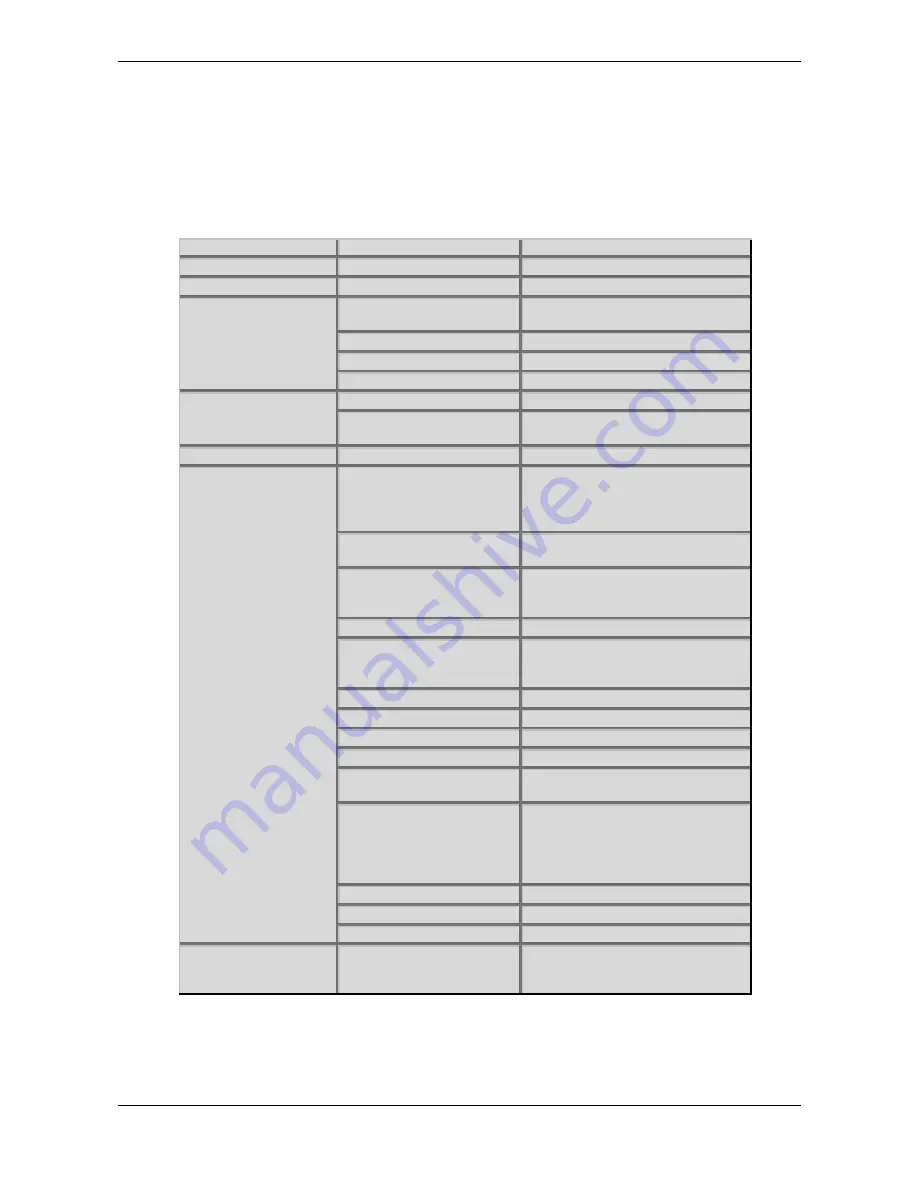
Section
Chapter
Sub-Chapter
Introduction
General Safety Guidelines
Power Supply
Setup and Connection
External Input
Switching off
Panic Function
Selecting Programs
Sound Selection by Category
Instruments and Sounds
all chapters
Basic Operation
Editing Parameters
all chapters
Multi Parameters
Ctrl W…Z
Multi Mode
Instrument Parameters
Selecting an Instrument for editing
Instrument settings
Step Sequencer
all chapters
The Tempo
Clock
Modulation Speed Levels
Xphorm
Oscillators
FM and FM Source
Wavetable Oscillators
Mixer
Balance
Noise / Ext. Balance
N/E Select F1 / F2 Feed
Routing
Filter
Selecting and Editing Filters
FM and FM Source
Pan, PanMod and PanMod Source
Filter Types
Comb + and Comb -
Effects
FX Types
Vocoder
all chapters
Arpeggiator Edit Menu
all chapters
Arpeggiator Edit Menu Step
Data
all chapters
Envelopes
Mode
ADS1DS2R Envelope
One Shot Envelope
LoopS1S2 Envelope
Loop All Envelope
LFOs
Sync, Fade, Clocked, Phase
Modulation Matrix
all chapters
Sound Parameters
Modifier Matrix
all chapters
Global Parameters
Global Menu
Global MIDI Channel, Sysex ID
Clock, Controller Send
Input Gain, Mix In parameter
Table 2:
Suggested chapters for synthesizer cracks
Summary of Contents for Q Rack
Page 1: ...User s Manual Q Keyboard Q Rack ...
Page 170: ...Appendix MIDI Implementation Chart Waldorf Q User s Manual 170 ...
Page 172: ......
Page 173: ......





























