-23-
6.3
Trouble check list
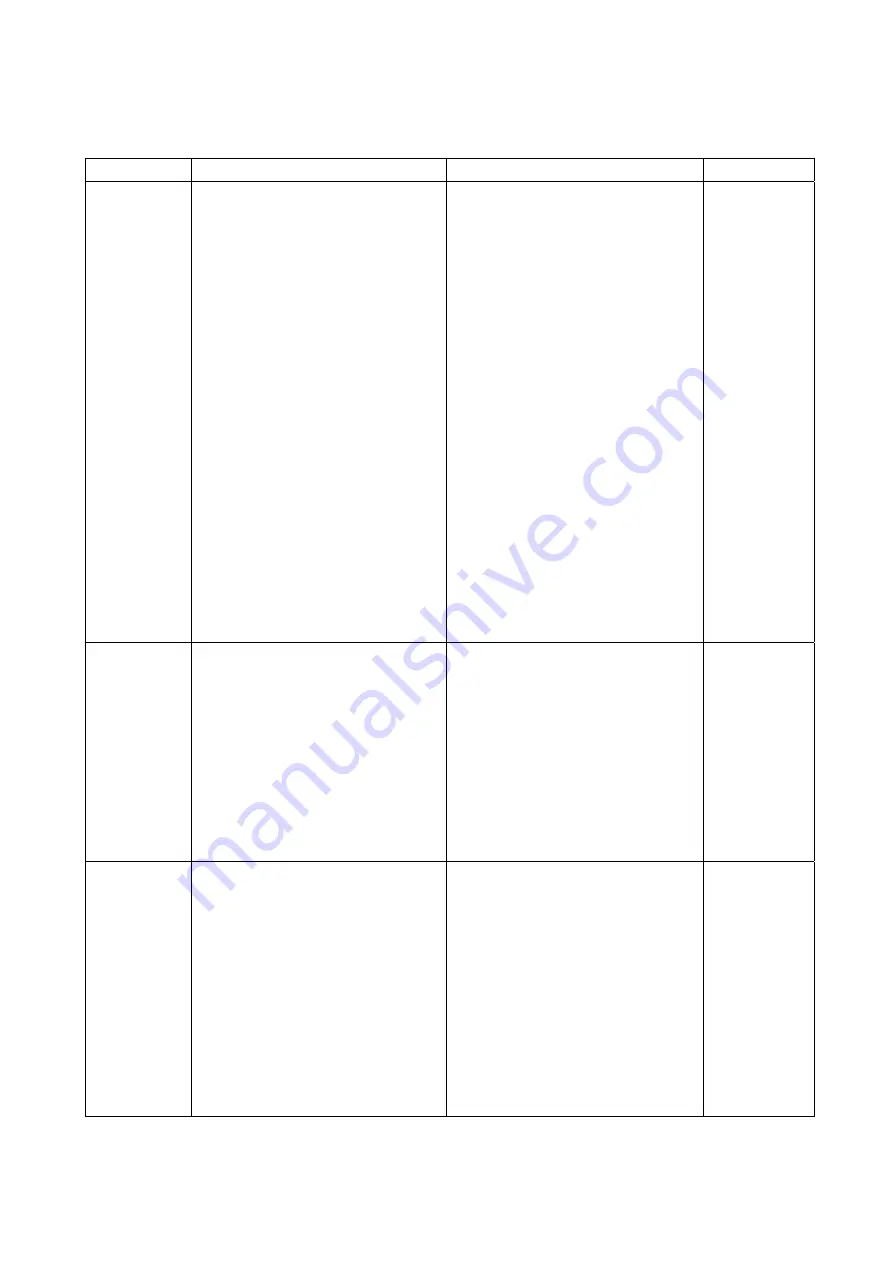
Table 7 Trouble check list
Problem Cause
Measures
Reference
①
The pump is not connected
to the power supply.
①
Connect the pump to the
power supply.
4.4
②
Problem with power supply
voltage
②
Set the power supply voltage
to within
±
10% of the rated
voltage.
4.5
③
The overload protector has
actuated.
③
Wait till the temperature
goes down to 78
±
9
℃
.
5.3
④
The motor malfunctions.
④
Replace the motor.
7
⑤
Low ambient temperature
has increased the oil
viscosity.
⑤
Increase the ambient
temperature to 0
℃
or more.
4.2
⑥
The entrance of foreign
matter into the pump caused
the rotor to burn out.
⑥
Overhaul (replace the
cylinder and rotor).
7
⑦
Moisture or solvents were
sucked in, forming rust
inside the pump.
⑦
Overhaul (replace the
cylinder and rotor).
7
⑧
Reaction product
accumulated in the pump
when the pump stops after
exhausting reactive gas.
⑧
Overhaul (clean the pump
inside and remove reaction
products).
7
The pump
does not
rotate.
⑨
Components inside the
pump have burnt out.
⑨
Overhaul (replace the
damaged components).
7
①
Problem with power supply
voltage
①
Set the power supply voltage
to within
±
10% of the rated
voltage.
4.5
②
Defective wiring to the pump
②
Perform wiring to the pump
again.
4.4
③
Low ambient temperature
has increased the oil
viscosity.
③
Increase the ambient
temperature to 0
℃
or more.
4.2
The pump’s
rotation is
unstable.
④
Foreign matter has entered
the pump.
④
Disassemble and clean the
pump to eliminate foreign
matter.
7
①
The pump is too small for
the volume of the vacuum
chamber.
①
Select another pump.
3.3
②
The pressure measurement
method is not correct.
②
Measure the pressure
correctly.
3.3
③
The vacuum gauge is not
suitable.
③
Measure with a calibrated
vacuum gauge suitable for
the pressure range.
The
pressure
does not
decrease.
④
The pipe connected to the
inlet port is small, or the
piping distance is long.
④
Use pipes having a diameter
larger than the inlet port
diameter, or reduce the
distance from the vacuum
chamber.
3.3





































