-9-
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
1.E-01
1.E+00
1.E+01
1.E+02
1.E+03
1.E+04
1.E+05
Outret Pressure-P2[Pa]
C
o
m
pr
ess
io
n
R
at
io
K=P
2
/P
1(
Q
1
=0
)
1×10
2
1×10
4
1×10
3
1×10
0
1×10
1
1×10
5
1×10
-1
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
1.E-02
1.E-01
1.E+00
1.E+01
1.E+02
1.E+03
1.E+04
1.E+05
Suction Pressure-P1[Pa]
P
um
pi
n
g
S
pee
d
[L
/m
in]
1×10
1
1×10
4
1×10
3
1×10
2
1×10
0
1×10
-1
1×10
-2
1×10
5
3.2 Fore
pump
.
A normal fore pump to combine to this mechanical booster pump is model
GLD-202(201) or GLD-137(136).
130
~
240L/min is most suitable for pumping speed.
Less than 10kPa are necessary for an ultimate pressure.
A normal fore pump is oil
rotary vacuum pump, but can use a diaphragm pump or a scroll pump, too.
However,
when outlet pressure runs in about 10kPa in succession, as for the gas temperature, it
is necessary to be pumps of structure to bear this high-temperature gas because it is
it with about 80 degrees Celsius.
3.3
Ultimate pressure
.
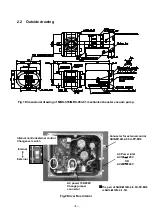
A mechanical booster pump ultimate pressure is decided on by pressure of a fore
pump.For example, become P=100/25=4.0Pa with a diaphragm pump of an ultimate
pressure of 100Pa than compression ratio property of Fig.4.
Also, the actual ultimate pressure of the vacuum device becomes higher than that
noted in the catalogue for the following reasons.
➀
The vacuum gauge is installed at a distance from the pump, and the steam and a
variety of gases are generated by water droplets and rust on the inside walls of
the pump and piping.
➁
Gasifying of volatile components which have dissolved in the pump oil.
(Deterioration of pump oil)
➂
Existence of a gas supply source including vacuum leakage in the vacuum path
3.4
Pumping speed
.
As for the pumping speed, be decided with fore pump pumping speed property and
compression ratio property.
Show a pumping speed curve of GLD-202(201) in Fig.5.
Fig.4 Compression ratio property
Fig.5 Pumping speed curve