15
Step 1:
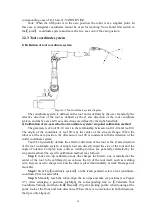
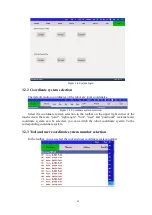
Determine the working space to be calibrated.
Step 2:
Move the robot with the operating tool to the origin of the coordinate system,
and record this point as point 1.
Step 3:
Move the robot with the operating tool to any point on the X axis of the
coordinate system, and record the point as point 2.
Step 4:
Move the robot with operating tool to any point in the XY plane that belongs
to the first quadrant, and record the point as point 3.
Step 5:
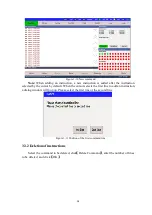
Click
【
Calculate
】
, then click
【
Save
】
.
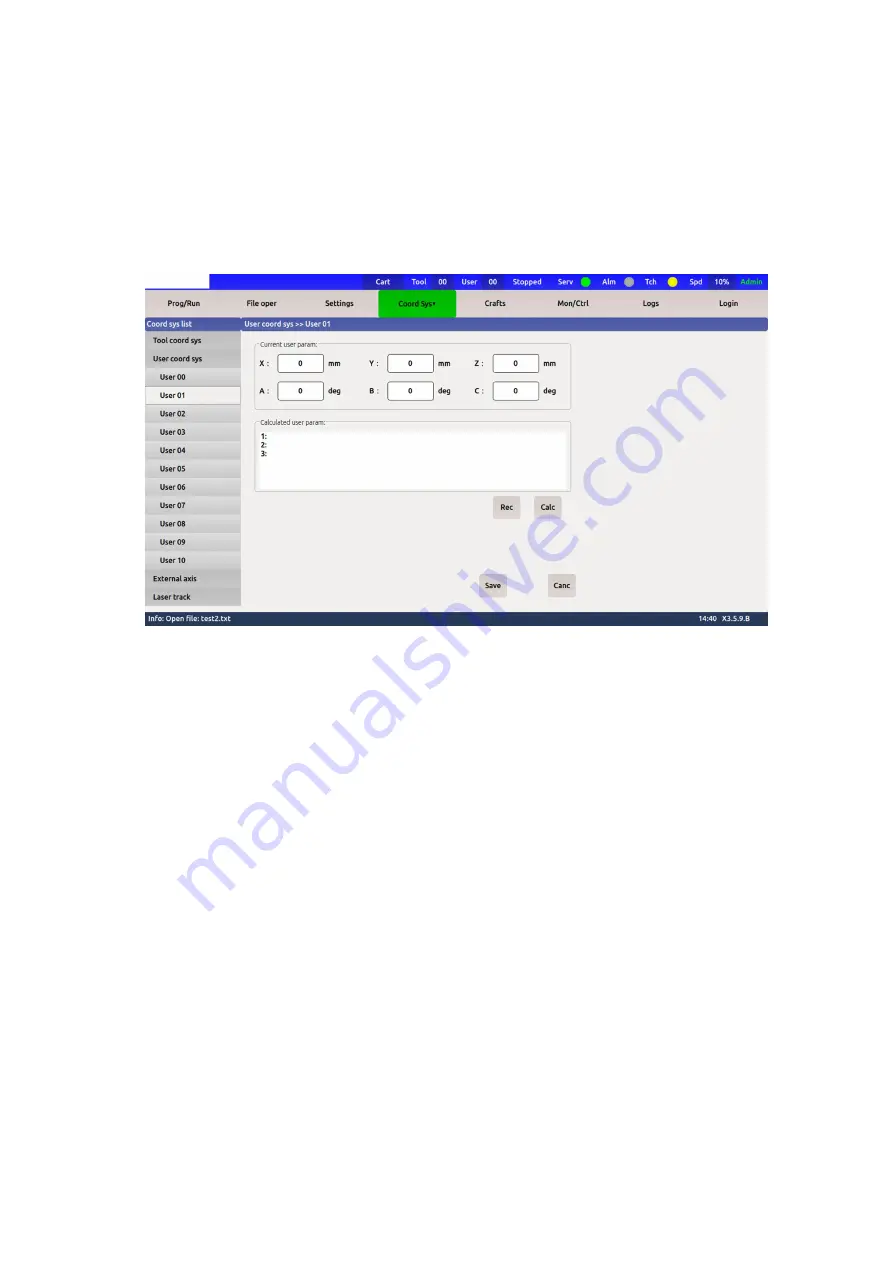
Figure 2-9 User coordinate system calibration
2.3 Robot zero point and calibration
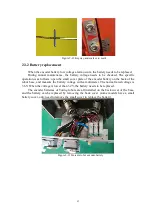
Turing industrial robots all use Ehercat bus-type servos, which rely on multi-turn
absolute encoders of servo motors to record positions. The multi-turn absolute encoder is
equipped with a 3.6V battery recording position, and there is no need to change it when
starting up. However, when the battery is empty and the battery is replaced, the robot
collides or the transmission component is replaced and the zero position is lost, it is
necessary to recalibrate the zero position and the joint parameters of the robot.
2.3.1 Robot zero
The zero attitude is the attitude where the joint value of each axis is 0. Zero
calibration is actually the default zero attitude of the calibration system and the actual zero
attitude of the robot.
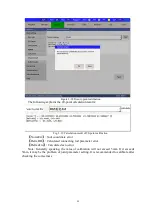
In
【
Parameter Setting
】
->
【
Basic Setting
】
->
【
Zero Calibration
】
, you can calibrate
the zero point.