Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany
TR-Electronic GmbH 2016, All Rights Reserved
10/31/2018
TR - ECE - BA - DGB - 0131 - 02
Page 69 of 103
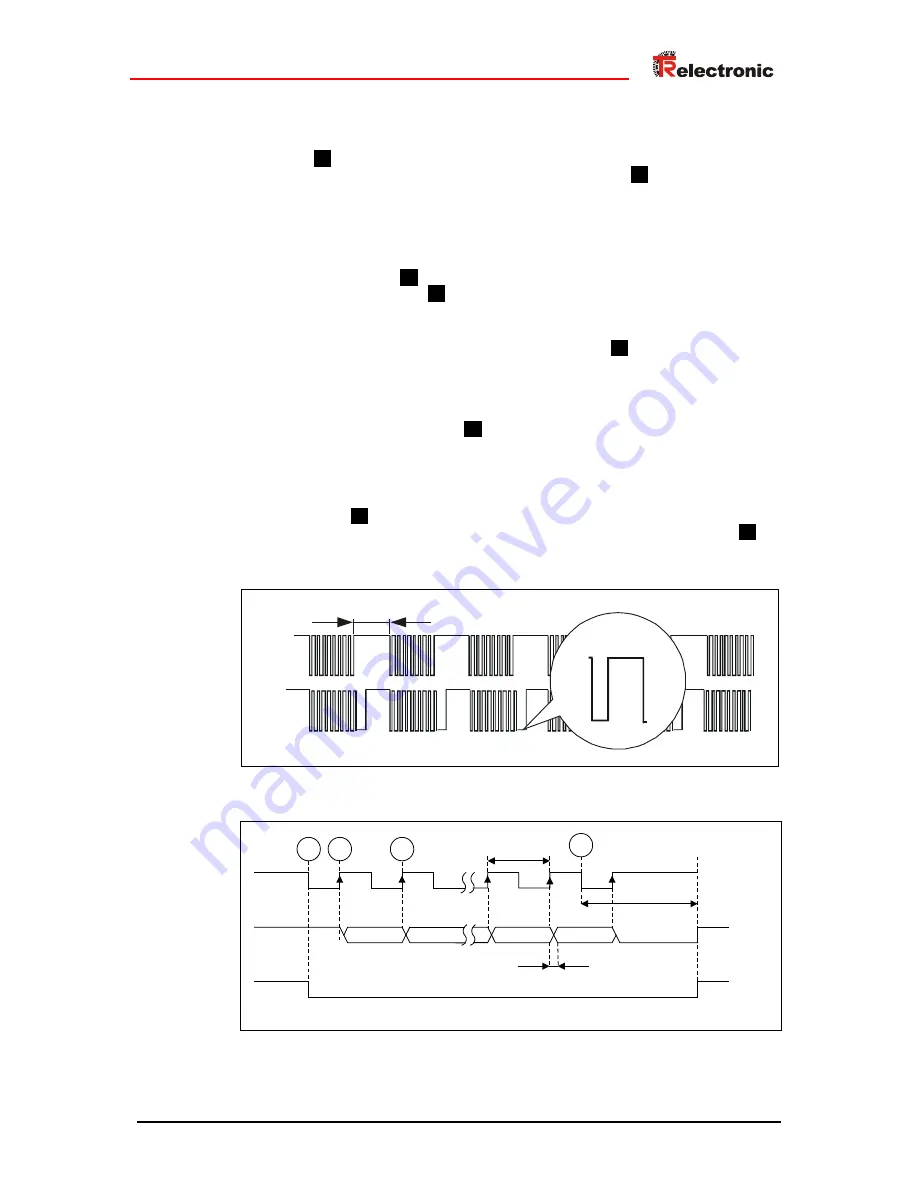
4.3.3 Data transmission
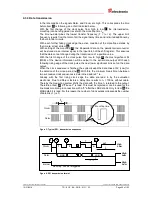
In the idle condition the signals Data+ and Clock+ are high. This corresponds the time
before item
(1)
is following, see chart indicated below.
With the first change of the clock pulse from high to low
(1)
the internal-device-
monoflop (can be retriggered) is set with the monoflop time t
M
.
The time t
M
determines the lowest transfer frequency (T = t
M
/ 2). The upper limit
frequency results from the total of all the signal delay times and is limited additional by
the built-in filter circuits.
With each further falling clock edge the active condition of the monoflop extends by
the time t
M
, at last at item
(4)
.
With setting of the monoflop
(1)
, the bit-parallel data on the parallel-serial-converter
will be stored via an internal signal in the input latch of the shift register. This ensures
that the data cannot change during the transmission of a position value.
With the first change of the clock pulse from low to high
(2)
the most significant bit
(MSB) of the device information will be output to the serial data output. With each
following rising edge of the clock pulse, the next lower significant bit is set on the data
output.
When the clock sequence is finished, the system keeps the data lines at 0V (Low) for
the duration of the mono period, t
M
(4)
. With this, the minimum break time t
p
between
two successive clock sequences is determined and is 2 * t
M
.
Already with the first rising clock edge the data are read in by the evaluation
electronics. Due to different factors a delay time results to t
V
> 100ns, without cable.
Thereby the measuring system shifts the data with the time t
V
retarded to the output.
Therefore at item
(2)
a "Pause 1" is read. This must be rejected or can be used for the
line break monitoring in connection with a "0" after the LSB data bit. Only to item
(3)
the
MSB data bit is read. For this reason the number of clock pulses corresponds the number
of data bits +1 (n+1).
Data+
Clock+
t
p
Monoflop time
Figure 3: Typical SSI - transmission sequences
Figure 4: SSI transmission format
t
M
LSB
MSB
Clock+
Data+
internal
Monoflop, can be retriggered
1
2
4
T
t
D
1
2
n
n+1
3
High
Low
High
Low
High
Low