87
Chapter 15
Specify Your Network Settings
•
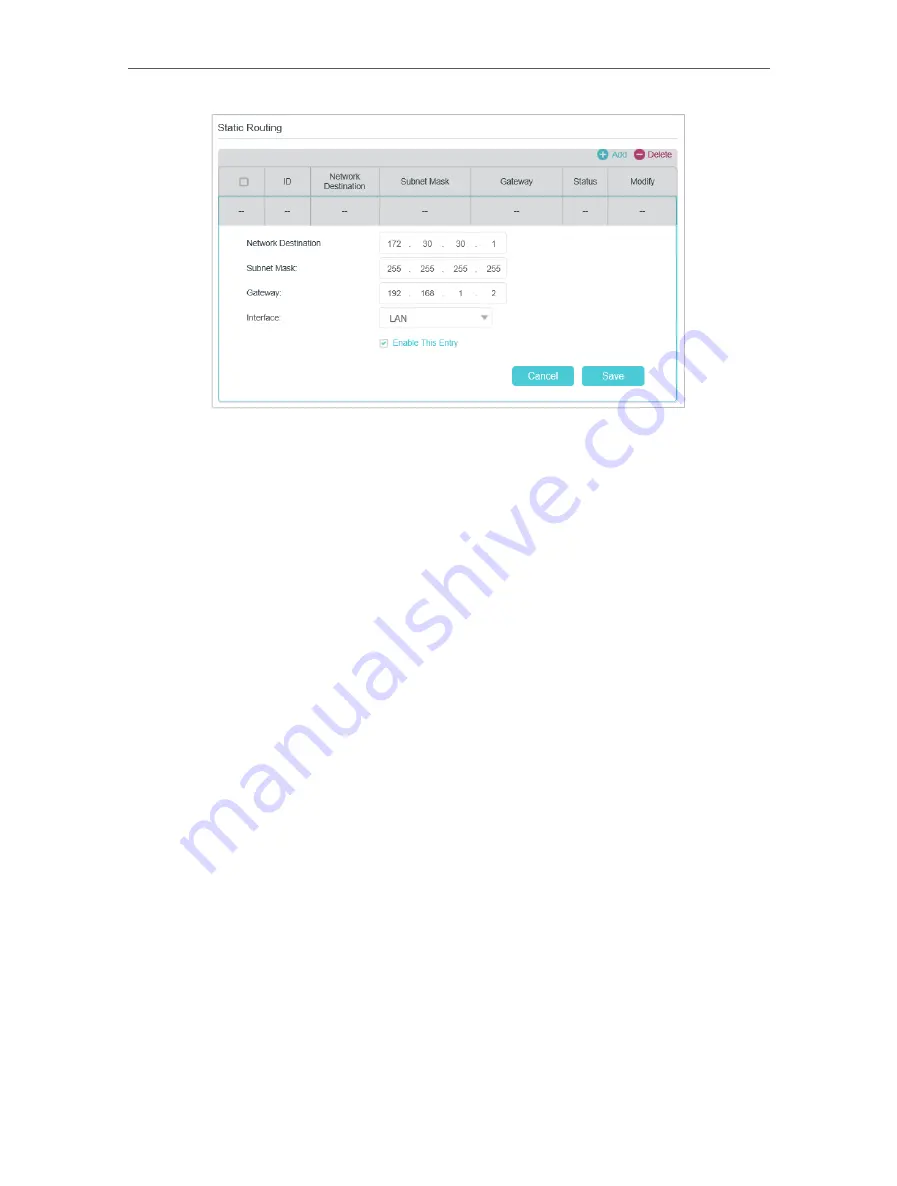
Network Destination:
The destination IP address that you want to assign to a static
route. This IP address cannot be on the same subnet with the WAN IP or LAN IP of the
router. In the example, the IP address of the company network is the destination IP
address, so here enters 172.30.30.1.
•
Subnet Mask:
Determines the destination network with the destination IP address.
If the destination is a single IP address, enter 255.255.255.255; otherwise, enter the
subnet mask of the corresponding network IP. In the example, the destination network
is a single IP, so here enters 255.255.255.255.
•
Gateway:
The IP address of the gateway device to which the data packets will be sent.
This IP address must be on the same subnet with the router’s IP which sends out the
data. In the example, the data packets will be sent to the LAN port of Router 2 and then
to the Server, so the default gateway should be 192.168.1.2.
•
Interface:
Determined by the port (WAN/LAN) that sends out the data packets. In the
example, the data is sent to the gateway through the LAN port, so LAN should be
selected.
5.
Select the check box to enable this entry.
6.
Click
OK
to save the settings.
Done!
Open a web browser on your PC. Enter the company server’s IP address to visit the
company network.
15. 6. Set Up the IPv6 Tunnel
The IPv6 Tunnel feature helps you obtain IPv6 resources based on an IPv4 WAN
connection or vice versa.
















































