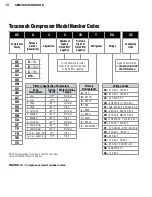
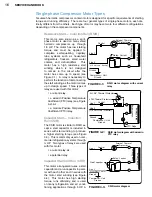
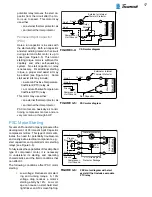
5
•
Use a pressure regulating valve and pressure gauges.
Commercial cylinders of nitrogen contain pressures in excess of 2000 psig at 70
°
F. At
pressures much lower than 2000 psig, compressors can explode and cause serious
injury or death. To avoid over pressurizing the system, always use a pressure-regulating
valve on the nitrogen cylinder discharge (see Figure 1-7). The pressure regulator must
be able to reduce the pressure down to 1 or 2 psig and maintain this pressure.
The regulating valve must be equipped with two pressure gauges:
»
one gauge to measure cylinder pressure, and
»
one gauge to measure discharge or downstream pressure.
•
Use a pressure relief valve.
In addition to a pressure regulating valve and gauges, always install a pressure relief
valve. This can also be a frangible disc type pressure relief device. This device should
have a discharge port of at least ½” MPT size. The valve or frangible disc device must
be set to release at 175 psig (see Figure 1-7).
•
Do not pressurize the system beyond 150 psig field leak test pressure.
When field testing a system for leaks, 150 psig is adequate test pressure.
• Disconnect nitrogen cylinder and evacuate the system before connecting the refrigerant
container.
Disconnect the nitrogen cylinder and evacuate the system according to the equipment
manufacturer's recommendations prior to charging the system.
System Charging
Failure to properly charge the system can result in serious injury or death from explosion or fire.
Follow these precautions when charging a system:
•
Do not operate the compressor without charge in the
system.
Operating the compressor without a charge in the
system can damage the hermetic terminal. As always,
to avoid serious injury or death from terminal venting
with ignition, never energize the compressor unless the
protective terminal cover is securely fastened.
•
Use proper refrigerant.
Use only the serial label refrigerant when charging
the system. Using a different refrigerant can lead to
excess system pressure and an explosion. Use of a
refrigerant other than the serial label refrigerant will void the compressor warranty.
•
Do not overcharge a refrigeration or air conditioning system.
Overcharging a refrigeration or air conditioning system can result in explosion. To avoid
serious injury or death, never overcharge the system. Always use proper charging
techniques. Limit charge amounts to those specified on the system equipment serial
label or in the original equipment manufacturer’s service information.
Overcharging the system immerses the compressor motor, piston, connecting rods,
and cylinders in liquid refrigerant. This creates a hydraulic block preventing the
compressor from starting. The hydraulic block is also known as locked rotor.
Continued supply of electricity to the system causes heat to build in the compressor.
This heat will eventually vaporize the refrigerant and rapidly increase system pressure.
If, for any reason, the thermal protector fails to open the electrical circuit, system
pressure can rise to high enough levels to cause a compressor housing explosion.
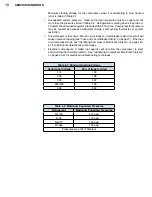
Gauges
To System
Relief Valve
Regulating
Valve
FIGURE 1-7
Dry nitrogen cylinder with
attached pressure gauges
needed for pressure testing
for leaks and purging.
Summary of Contents for AH5540E
Page 1: ...Hermetic Compressor Service Handbook Wholesale Distribution North America...
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...Hermetic Compressor Service Handbook Ann Arbor MI 48108 REV 3 11...
Page 4: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 9: ...Chapter 1 General Service Safety Precautions...
Page 16: ......
Page 17: ...Chapter 2 Model and Application...
Page 22: ......
Page 23: ...Chapter 3 Compressor Motor and Component...
Page 36: ......
Page 37: ...Chapter 4 Servicing...
Page 38: ...30 SERVICE HANDBOOK...
Page 79: ...71...
Page 80: ......
Page 81: ...Chapter 5 Installation and Replacement...
Page 96: ......
Page 97: ...Liquid refrigerant migration to compressor FIGURE 6 1 Chapter 6 Operation...
Page 108: ......
Page 109: ...Appendix...
Page 113: ...105 Reciprocating Compressor FIGURE A 2 Internal view of typical air conditioning compressor...
Page 118: ...110 SERVICE HANDBOOK Notes...
Page 119: ......