DocID022729 Rev 5
25/70
L6472
Functional description
70
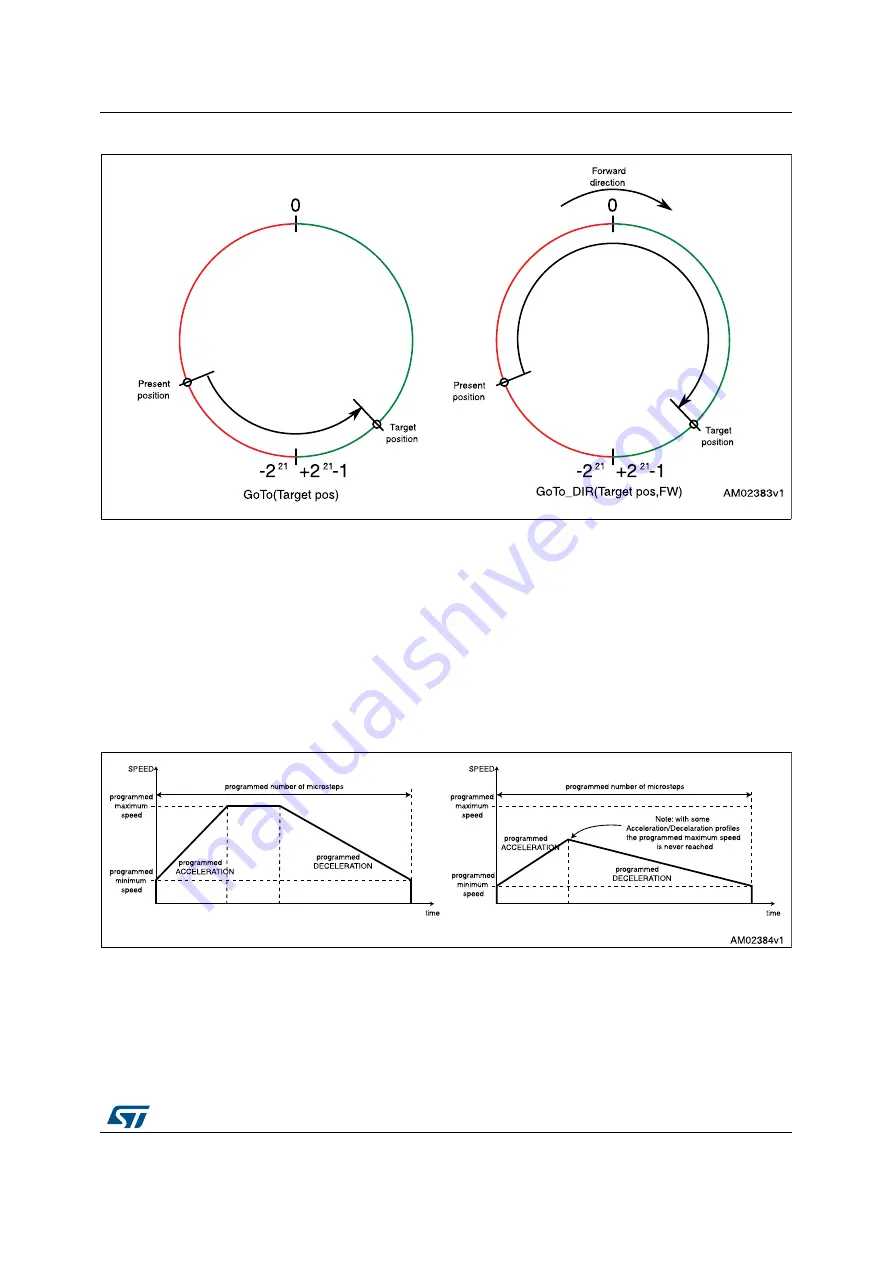
Figure 9. Positioning command examples
6.7.3 Motion
commands
Motion commands produce a motion in order to perform a user-defined number of
microsteps in a user-defined direction that are sent to the device together with the command
(see
The performed motor motion is compliant to programmed speed profile boundaries
(acceleration, deceleration, minimum and maximum speed).
Note that with some speed profiles or motion commands, the deceleration phase can start
before the maximum speed is reached.
Figure 10. Motion command examples
6.7.4 Stop
commands
A stop command forces the motor to stop. Stop commands can be sent anytime.
The SoftStop command causes the motor to decelerate with a programmed deceleration
value until the MIN_SPEED value is reached and then stops the motor maintaining the rotor
position (a holding torque is applied).