3-7
C
ONFIGURING
AND
T
ESTING
THE
N
ETWORK
C
ARD
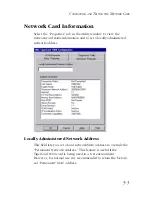
An IEEE 802.1Q VLAN is a group of ports that can be located
anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they
belong to the same physical segment. VLANs help to simplify
network management by allowing you to move devices to a new
VLAN without having to change any connections. VLANs can be
easily organized to reflect departmental groups (such as Marketing
or R&D) or usage groups (such as e-mail or video conferencing).
VLANs provide greater network efficiency by reducing broadcast
traffic, but also allow you to make network changes without
having to update IP addresses or IP subnets. VLANs inherently
provide a high level of network security, since traffic must pass
through a router or a Layer 3 switch to reach a different VLAN.
Usually VLANs are configured within IEEE 802.1Q VLAN-enabled
switches in the network where ports are assigned to specific
VLAN IDs. The TigerCard 1000 allows up to 16 VLAN IDs to be
configured directly within the card, so a network server can share
its resources with up to 16 VLANs through just one switch link.
This avoids the expense of having multiple adapters in a server,
and significantly reduces the latency between clients and the
server.
Note:
The VLAN IDs configured within the card must match
those in the IEEE 802.1Q-compliant switches throughout
the network. Also, the card must be attached to a switch
port that permits overlapping VLANs.
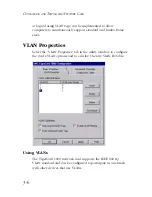
Traffic Priority
The TigerCard 1000 network card supports the IEEE 802.1p
Quality of Service standard. Each VLAN is assigned a priority level
in the VLAN ID table. Defining priority levels in the network card
allows it to work with other network devices to deliver higher
priority packets first.
Summary of Contents for TigerCard 1000
Page 19: ...1 10 INSTALLING THE NETWORK CARD ...
Page 35: ...2 16 INSTALLING NETWORK DRIVERS ...
Page 51: ...B 2 CABLES ...
Page 57: ...INDEX Index 4 ...