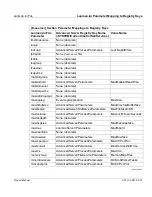
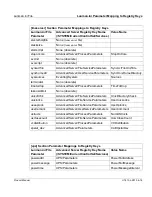
Glossary
Product Manual
U7613-J-Z815-6-76
©
S
iem
e
n
s
N
ix
d
or
f I
n
fo
rm
at
io
n
s
s
y
s
tem
e
A
G
1
995
P
fad:
D:
\O
76
13
e6\
u7
61
3e.
m
ix
timesource
An Advanced Server for UNIX service which identifies a
server
as a timesource
for a domain. Other
servers
and
clients
can synchronize their clocks with the
timesource. Exception: systems with UNIX cannot be synchronized.
timesource server
The server with the timesource service, which therefore serves as the
timesource
of the
local network.
The other
servers
and
clients
in the network synchronize
themselves with the timesource server. An Advanced Server for UNIX server
can only operate as a timesource server and not as a synchronized server.
trust relationship
Trust relationships are links between domains that enable pass-through
authentication, in which a trusting domain honors the logon authentications of
a trusted domain. With trust relationship, a user who has only one user account
in one domain can potentially access the entire network. User accounts and
global groups defined in a trusted domain can be given rights and resource
permissions in a trusting domain, even though those accounts do not exist in
the trusting domain’s directory database.
user account
Consists of all the information that defines a user to the Advanced Server. This
includes items such as the user name and password required for the user to log
on, the groups in which the user account has membership, and the rights and
permissions the user has for using the system and accessing its resources. For
the Advanced Server, user accounts are managed with User Manager for
Domains. See also
group
.
user account database
The data of the user accounts and the established groups is stored in the
Advanced Server for UNIX databases. See also
user account
and
group
.
user level security
A type of security which manages a
user account
for each user. Each user then
maintains rights for specific
shared resources
which describe which actions each
user can operate with each resource. See also
password
.
username
Every user receives a unique name within a
local network
. Users use this name
to log on to a
server
and to identify themselves.