°
A slave address that is free in the Modbus network
°
A slave address that the master expects
•
The same baud rate must be set in the GLS100 as in the master.
The following parameters are factory set on the GLS100:
•
Slave address: 10
•
Baud rate: 19,200 bps
•
Parity: Even
The following communication parameters can be allocated to the GLS100:
•
Slave address: 1 to 247 (0 is generally assigned to the master)
•
Baud rate:
0: 1,200 bps
1: 2,400 bps
2: 4800 bps
3: 19,200 bps
4: 19,200 bps
5: 38,400 bps
6: 57,600 bps
7: 115,200 bps
7.4.2
Basic information about Modbus and reading out code information
Modbus is based on RS-485 with a Modbus RTU protocol structure. Data exchange is
always based on requests from the master and responses from the slave devices. The
respective request/response string looks like this:
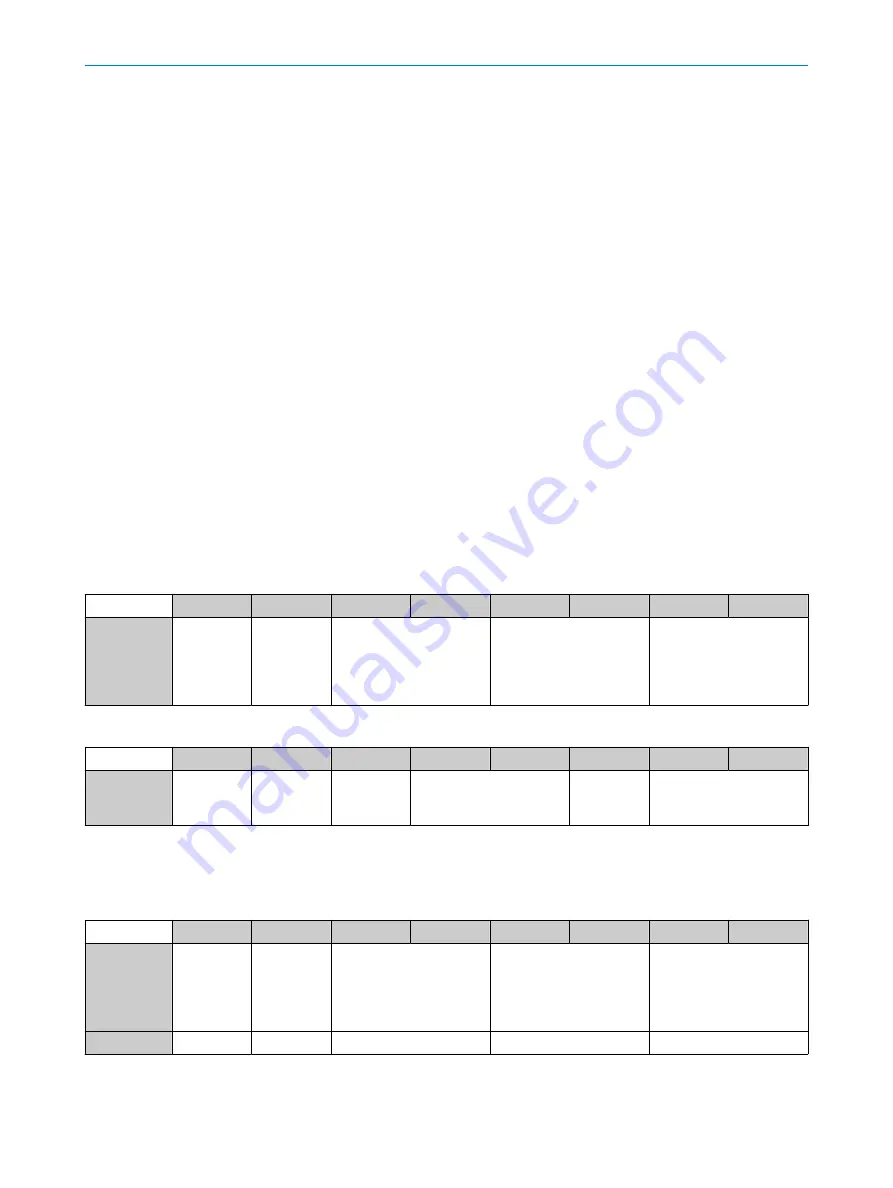
Request
Byte
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ModBus con‐
tents
Slave
Address
“Function
code” e.g.
0x04 Read
“Input regis‐
ters”
Readout: Start address
(16 bit unsigned)
Readout: Number register
N (16 bit unsigned)
Checksum (16 bit
unsigned)
Response
Byte
0
1
2
3
4
2xN+5
2xN+6
2xN+7
ModBus con‐
tents
Slave
Address
Response:
“Function
code” 0x04
Number of
bytes, 2xN
Start register
Register
contents
Checksum (16 bit
unsigned)
The relevant code information is provided in “Section result data”. Read it out periodically (not more often than
every 50 ms) (addresses 320 to 331) using "Modbus function code #4":
Example
Byte
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ModBus con‐
tents
Slave
Address
“Function
code” e.g.
0x04 Read
“Input regis‐
ters”
Readout: Start address
(16 bit unsigned)
Readout: Number of regis‐
ters (16 bit unsigned)
Checksum (16 bit
unsigned)
Value (hex)
0x0A
0x04
0x0140
0x000C
0xF15C
7
COMMISSIONING
28
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | GLS100
8026282/2021-05-26 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
















































